Safety supervisors play a crucial role in ensuring a safe and healthy work environment for employees. Their duties and responsibilities encompass various aspects of workplace safety, including risk assessment, hazard identification, training, and enforcement of safety protocols. In this article, we will explore the key duties and responsibilities of safety supervisors and how they contribute to achieving high performance of safety in the workplace.
Also Read: Guideline for Process Safety Management Program with Free Training

1. Conducting Risk Assessments and Hazard Identification
Safety supervisors are responsible for conducting thorough risk assessments and identifying potential hazards within the workplace. This involves regularly inspecting work areas, equipment, and processes to identify any potential risks or hazards that could endanger employees’ safety. By proactively identifying and addressing these hazards, safety supervisors help prevent accidents and injuries.
Safety supervisors typically follow a systematic process to conduct risk assessments in the workplace. The steps involved in conducting a risk assessment may include the following:
- Identify hazards: Safety supervisors begin by identifying potential hazards in the workplace. This involves examining the physical environment, work processes, equipment, and materials used. They may review incident reports, conduct site inspections, and consult with employees to identify known hazards and potential risks.
- Assess the likelihood and severity of risks: Once hazards are identified, safety supervisors assess the likelihood of those hazards causing harm and the severity of the potential consequences. This evaluation considers factors such as the frequency of exposure, the potential severity of injuries or incidents, and the number of people at risk.
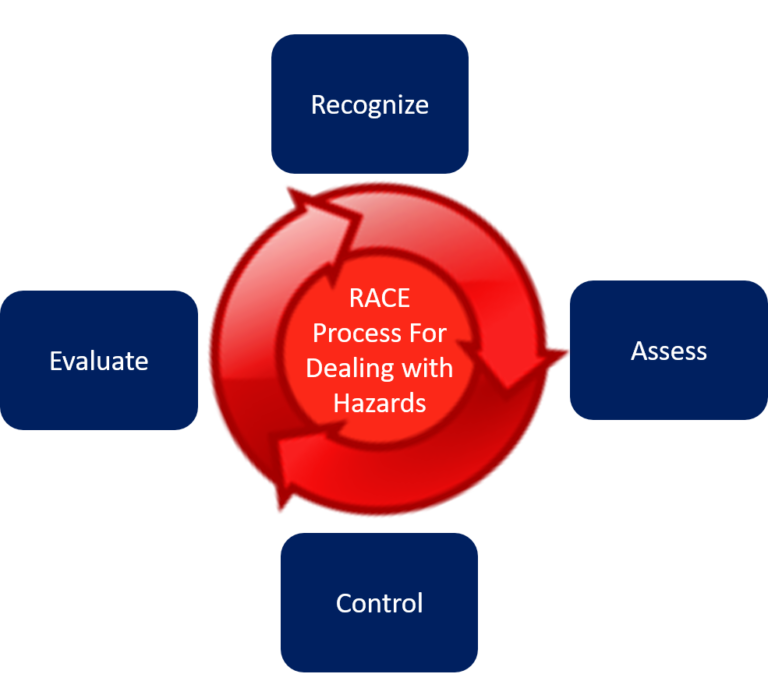
- Evaluate current controls: Safety supervisors review existing safety measures and controls in place to mitigate the identified risks. This includes examining administrative controls (policies, procedures, training), engineering controls (physical barriers, ventilation systems), and personal protective equipment (PPE). They assess the effectiveness of these controls in reducing or eliminating the identified risks.
- Determine risk levels: Based on the likelihood and severity assessments, safety supervisors assign risk levels to each identified hazard. This helps prioritize risks and determine the appropriate actions needed to manage them. Common methods for rating risk levels include using a numerical scale or a color-coded system.
- Develop control measures: Safety supervisors develop control measures to eliminate or reduce the identified risks. This may involve implementing engineering controls, modifying work processes, providing additional training, or updating policies and procedures. The goal is to implement effective measures that minimize or eliminate the likelihood and severity of the identified risks.
- Implement and communicate control measures: Safety supervisors ensure that the identified control measures are effectively implemented in the workplace. They communicate the changes to employees, provide necessary training and resources, and monitor compliance with the new controls.
- Review and monitor: Risk assessments are not one-time activities. Safety supervisors regularly review and monitor the effectiveness of the implemented control measures. They conduct periodic inspections, evaluate incident reports, and gather feedback from employees to identify any new hazards or changes in the workplace that may require updated risk assessments.
Also Read More : The Essentials of Job Safety Analysis and Risk Assessment
2. Developing and Implementing Safety Procedures and Protocols
Safety supervisors are responsible for developing and implementing safety procedures and protocols that comply with relevant regulations and industry standards. They ensure that employees are aware of these procedures and provide appropriate training to ensure their understanding and adherence. By establishing clear guidelines and protocols, safety supervisors promote a culture of safety and reduce the likelihood of accidents or incidents.
3. Providing Safety Training and Education
Safety supervisors are responsible for providing comprehensive safety training and education to employees. This includes initial onboarding training for new employees, as well as ongoing training to ensure that all employees are aware of safety protocols and best practices. Safety supervisors may conduct training sessions themselves or coordinate with external trainers or subject matter experts. They focus on topics such as hazard recognition, proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE), emergency response procedures, and safe work practices. By investing in employee training, safety supervisors empower employees to actively participate in maintaining a safe work environment.
4. Enforcing Safety Policies and Regulations
Safety supervisors are responsible for enforcing safety policies and regulations within the workplace. They monitor employee compliance with safety protocols and promptly address any violations or non-compliance. This may involve conducting regular inspections, observing work practices, and taking corrective actions as necessary. Safety supervisors also collaborate with management to implement disciplinary measures when employees repeatedly disregard safety guidelines. By consistently enforcing safety policies, safety supervisors create a culture of accountability and ensure that safety remains a top priority for everyone in the workplace.
Read Also : Photo of the day: Unsafe Conditions(Opens in a new browser tab)
5. Conducting Safety Inspections and Audits
Safety supervisors regularly conduct safety inspections and audits to evaluate the effectiveness of safety measures and identify areas for improvement. These inspections involve assessing the physical condition of the workplace, equipment maintenance, and employee adherence to safety protocols. Safety supervisors also review incident reports and near-miss incidents to identify any underlying safety issues. Based on their findings, they develop action plans to address identified deficiencies, implement corrective measures, and monitor their effectiveness. Regular safety inspections and audits help ensure that safety standards are consistently maintained and improved.
Read Also : Conduct a Proper Safety Audit(Opens in a new browser tab)
6. Investigating Accidents and Incidents

Incident investigation and reporting is a crucial responsibility of safety supervisors. When accidents, injuries, or near-miss incidents occur in the workplace, safety supervisors conduct thorough investigations to determine the root causes and contributing factors. The process typically involves the following steps:
- Secure the scene: Safety supervisors first ensure that the incident scene is safe and secure. They may take necessary precautions, such as isolating the area or providing immediate medical assistance to injured individuals.
- Gather information: Safety supervisors gather relevant information about the incident. They interview witnesses, affected employees, and supervisors to obtain firsthand accounts of what happened. They collect any available documentation, such as work procedures, equipment manuals, or maintenance records, to gain a comprehensive understanding of the circumstances surrounding the incident.
- Document evidence: Safety supervisors document evidence related to the incident. This may include taking photographs, collecting samples, or preserving physical evidence. They ensure that all evidence is properly handled and stored to maintain its integrity.
- Analyze the incident: Safety supervisors analyze the gathered information and evidence to identify the root causes and contributing factors of the incident. They examine factors such as equipment failures, human errors, environmental conditions, training deficiencies, or organizational issues that may have played a role in the incident.
- Determine corrective actions: Based on the analysis, safety supervisors determine appropriate corrective actions to prevent similar incidents from occurring in the future. They develop practical and effective measures, such as improved training programs, enhanced safety procedures, equipment modifications, or organizational changes.
- Report writing: Safety supervisors prepare comprehensive incident reports that document the findings of the investigation. The reports include a detailed description of the incident, the identified root causes, contributing factors, and recommended corrective actions. The reports are typically submitted to relevant stakeholders, such as management, regulatory agencies, or safety committees.
- Follow-up and implementation: Safety supervisors ensure that the recommended corrective actions are implemented in a timely manner. They may collaborate with different departments or individuals to monitor the progress of implementation and provide necessary guidance or support.
- Continuous improvement: Incident investigation and reporting are not only about addressing immediate issues but also about learning from incidents to prevent future occurrences. Safety supervisors may analyze trends and patterns from incident reports to identify overarching safety concerns and develop strategies for continuous improvement in safety practices and procedures.
By effectively conducting incident investigations and reporting, safety supervisors contribute to creating safer work environments, preventing future incidents, and improving overall safety performance in the workplace.
Corrective Action
Corrective action that a safety supervisor might recommend based on the findings of an incident investigation:
Example: Following an incident where an employee slipped and fell on a wet floor in a manufacturing facility, the safety supervisor conducts an investigation and identifies the following root causes and contributing factors:
- Inadequate housekeeping practices: The investigation reveals that the floor was wet due to a leaking pipe, and there were no proper procedures in place to promptly address such issues.
Based on these findings, the safety supervisor might recommend the following corrective action:
- Corrective Action: Implement a comprehensive housekeeping program and improve maintenance procedures.
- Develop and communicate clear procedures: Establish clear procedures for reporting and addressing maintenance issues promptly, including leaks, spills, or other potential hazards. Ensure that employees are aware of the reporting process and understand their responsibility to promptly report any hazards they observe.
- Regular inspections: Conduct regular inspections of the workplace to identify and address potential hazards, including checking for leaks, spills, or other sources of water accumulation. Assign responsibility to designated personnel for conducting inspections and promptly addressing identified issues.
- Enhanced training: Provide training to employees on proper housekeeping practices, emphasizing the importance of maintaining clean, dry floors and promptly reporting any hazards they encounter. Include information on the procedures for reporting maintenance issues and the potential risks associated with slip and fall incidents.
- Implement preventive maintenance program: Establish a preventive maintenance program to proactively address potential equipment failures or leaks that could lead to hazardous conditions. Regularly inspect and maintain plumbing systems, equipment, and infrastructure to prevent water leaks or spills.
- Communication and signage: Clearly communicate and enforce the use of signage to indicate wet floors or potential hazards. Ensure that appropriate warning signs are readily available and effectively placed in areas where spills or wet floors are likely to occur.
- Continuous monitoring and feedback: Regularly monitor the effectiveness of the implemented corrective actions and gather feedback from employees. Encourage employees to provide suggestions for improvement and actively engage them in the ongoing maintenance and housekeeping efforts.
By implementing these corrective actions, the safety supervisor aims to address the root causes and contributing factors identified in the incident investigation, thereby reducing the risk of slip and fall incidents and promoting a safer work environment.
Read more: Photo of the day: Incident Investigations
7. Promoting Safety Awareness and Communication
Safety supervisors actively promote safety awareness and foster a culture of open communication within the workplace. They organize safety meetings, toolbox talks, and safety campaigns to educate employees about potential risks and the importance of safety. Safety supervisors encourage employees to report any safety concerns or near-miss incidents, ensuring that potential hazards are promptly addressed. They also facilitate communication channels for employees to provide feedback and suggestions regarding safety improvements. By promoting safety awareness and open communication, safety supervisors create a positive safety culture where employees actively participate in maintaining a safe work environment.
8. Stay updated on regulations and industry standards
Safety supervisors keep themselves updated on relevant safety regulations, codes, and industry best practices. They attend training programs, seminars, and conferences to stay informed about new developments in safety practices and technologies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, safety supervisors play a crucial role in achieving high performance of safety in the workplace. Through their duties and responsibilities, they contribute to creating a safe and healthy work environment, reducing accidents and injuries, and fostering a culture of safety among employees. By conducting risk assessments, developing and implementing safety procedures, providing training, enforcing regulations, conducting inspections and audits, investigating accidents, and promoting safety awareness and communication, safety supervisors ensure that safety remains a top priority in the workplace.
Read Also : Photo of the day: Outline Safety observations
For more safety Resources Please Visit Safetybagresources



