Personal Protective Equipment for Chemical, Biological, and Radiological Hazards Design, Evaluation, and Selection by EFG Dickson. (PPE) is essential for individuals who are working in environments where they may be exposed to chemical, biological, radiological, or nuclear (CBRN) hazards. PPE is a barrier between the wearer and the hazardous materials, protecting the individual from harm. In the case of CBRN hazards, the intent of use is typically malicious, such as in acts of terrorism or combat situations. PPE designed for CBRN protection must be able to protect against a variety of different agents, including nerve agents, biological toxins, and radioactive particles. While the focus of the book may be on protection against the deliberate use of CBRN agents, the same PPE may also be helpful in a workplace setting where CBRN agents are handled. In such settings, employers have a responsibility to provide appropriate PPE to protect their workers from potential exposure. It is important to note that PPE alone may not be sufficient to provide complete protection against CBRN hazards. Proper training, decontamination procedures, and emergency response plans must also be in place to ensure the safety of those working in these environments.
Also Read: Biological Hazard Control
SNAP of THE BOOK
WHAT IS CBRN PPE AND WHY IS IT USED?
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is equipment worn to protect the wearer from some external hazard: in this case, chemical, biological, radiological, or nuclear hazards, all of which can be considered to be toxic. The term CBRN, an acronym for “chemical, biological, radiological, and nuclear,” is used here to describe the particular combination of the hazardous environment and the intent of use. The book is focused primarily on protection against the deliberate use of CBRN agents in a terrorism or combat environment. The same PPE may be useful in a workplace setting in which CBRN agents are handled; however, as we discuss later, this results in some potentially important distinctions in the concept of the use of the equipment.
Also Read: Chemical Risk Assessment form

CBRN PPE almost always has protective or operational requirements in addition to its CBRN protective functions. In most cases, however, CBRN protection is deemed a primary requirement, with the other requirements superimposed once CBRN protection is provided. CBRN protective equipment may be designed to be worn by:
- Those responding to the use of CBRN agents (e.g., first or later responders)
- Those who are expected to perform their normal functions despite the fact that CBRN agents have been used (e.g., the military)
- Those who are being provided with emergency protection for escape purposes (e.g., civilians located in the vicinity)
In addition, CBRN protective equipment may be worn by those who are performing activities such as remediation, demilitarization, or laboratory investigation, where the environment is more controlled but the possibility of exposure to CBRN agents still
exists. Protection against toxic materials has often been treated, conceptually, as an “all or nothing” idea—a person is either protected totally or is not protected at all.
Also Read: E-Books: Biological Risk Engineering Handbook Infection Control and Decontamination
As we shall see, this approach is both overly simplistic and counterproductive. The degree of protection required is dependent on many factors, and protection needs not to be “total” to be effective; however, the protection requirements and expected performance must be well understood, and limitations and the use of the equipment must be well-defined. A number of issues need to be considered to understand protection requirements. The first is the nature of the hazard for which protection must be provided.
WHAT ARE CBRN AGENTS?
CBRN agents consist of any chemical, biological, or radiological/nuclear substance that can be deliberately employed to cause harm to unprotected persons [1,2]. Chemicals may cause damage as a result of specific chemical reactions that happen when the body is exposed to them, disrupting bodily functions. Biological agents are living microorganisms that cause disease. Radiological agents (which may either result from a nuclear explosion or themselves be used) will damage living systems as a result of high-energy radiation interactions. CBRN agents may range from military agents, which have been designed or chosen to be particularly effective when used in a deliberate attack, to toxic industrial chemicals, which may be available more readily or in larger quantities.
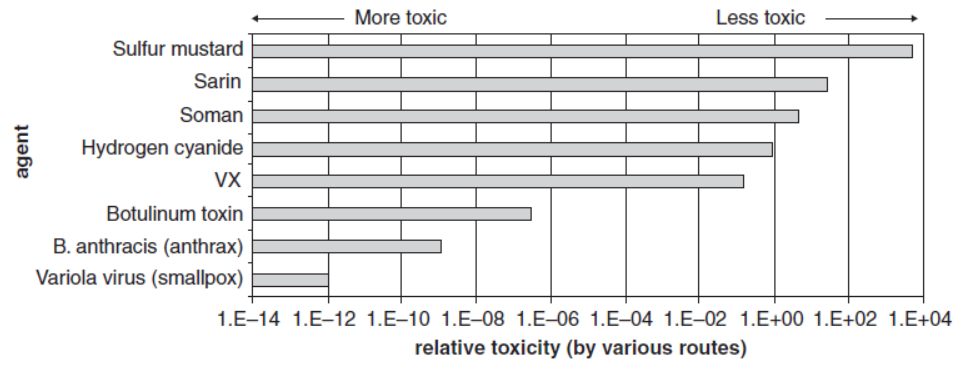
There are a number of additional distinctions between C, B, and R/N agents: in terms of how they act on the body, their relative toxicity (Figure 1-1), and how they may be delivered, which is discussed in Chapter 2; nevertheless, it is apparent that they can all be described in general terms as materials that may be hazardous when the body is exposed to them, and there are a number of generic ways in which these
hazards can be described, regardless of the class of agent. The most important aspect of these materials in the context of CBRN protection is the idea of deliberate use.
Deliberate use implies the features outlined in Table 1-1 compared with those of an
accidental release.
Also Read: Enhancing performance & health and safety culture
Contents
The content of PPE for Chemical, Biological, and Radiological Hazards
- What Is CBRN PPE and Why Is It Used
- Context of Use as It Relates to Design, Selection
- Hazardous Substances
- Radiation Hazards and Respiratory Hazards
- Biological Hazards
- Types of Short- and Long-Term Effects
- Radiation Exposure
- Designing for Appropriate Protection and Performance
- Barrier Materials and Hardening
- Protective Equipment: Concepts, Components, and Systems
- Performance Evaluation and Standard Test Methods
- Selection and Use of PPE
- Operational Requirements
- Performance and Selection Standards and Regulations
- North America, Europe, Asia, ISO, NATO
Also Read: Tips for Chemical spills Preparation and Incident Response
You can Download Other safety Resources at https://safetybagresources.com/
Download the book
E-Books: PPE for Chemical, Biological, and Radiological Hazards
More Downloads
- E-Books: Healthcare Hazard Control & Safety Management
- E-Books: Safety, Health and Working Conditions Training Manual
- E-Books: Energy Efficiency in Water and Wastewater Facilities
- E-Books: Fire Service Features of Buildings and Fire Protection Systems
- E-Books: Evaluation of Fire Safety free download
- E-Books: PPE for Chemical, Biological, and Radiological Hazards free
- E-Books: Changing the Workplace Safety Culture free download
- E-Books: Site Emergency Planning Workbook
- E-Books: Load Restraint Guide
- E-Books: Essential Practices for Creating, Strengthening, and Sustaining Process Safety Culture
- E-Books: System Safety Engineering and Risk Assessment
- E-Books: Permit-Required Confined Spaces
- E-Books: Is it Safe to Enter Confined Space?
- E-Books: 5-Minute Workplace Safety Talks
- E-Books: Safety Culture and High-Risk Environments
- E-Books: Practical Guide to Industrial Safety
- E-Books: Slip, Trip, and Fall Prevention for Healthcare Workers
- E-Books: Health and Safety at Work Key Terms
- E-Books: Fundamentals of Process Safety Engineering
- E-Books: Gas Detection Hand Book
- E-Books: Occupational health and safety management systems ANSI-AIHA-z10-2012
- E-Books: Hot Work on Drums and Tanks
- E-Books: Human Fatigue Risk Management
- E-Books: Guidelines for the provision of facilities and general safety in the construction industry
- E-Books: Handbook of Training in Mine Rescue and Recovery Operations ( 2021)
- E-Books: Code of Practice for the Safe Use of Lifting Equipment – Edition 9 (Nov 2019)
- E-Books: Free Forklift Health and Safety Best Practices Guideline
- E-Books: Handbook of Hazardous Chemical Properties
- E-Books: Human Performance Improvement through Human Error Prevention
- E-Books: Principles Of Fire Risk Assessment In Buildings
- E-Books: Investigation of Occupational Accidents and Diseases
- E-Books: Radiation Protection and Safety in Industrial Radiography
- E-Books: Basic Guide to System Safety, Third Edition
- E-Books: Food Safety Management-A Practical Guide for the Food Industry
- E-Books: Safety identification: Escape and evacuation plan signs- ISO 23601
- E-Books: Safety at Work
- E-Books: The Safety-Critical Systems Handbook 4th edition
- E-Books: Fundamental principles of occupational health and safety
- E-Books: Fire Safety Risk assessment Guide – Sleeping Accommodation
- E-Books: Mental health at work series
- E-Books: Live Fire Training: Principles and Practice
- E-Books: Pre-Startup Safety Review Guide
- E-Books: Fire and Emergency Drill Manual and Building Inspection Guide
- E-Books: Health and Safety: Risk Management 5th edition
- E-Books: Fire Protection systems -Third edition 2021
- E-Books: Fire Safety Logbook templates
- E-Books: From Accidents to Zero
- E-Books: Electric Safety Practice and Standards
- Your steps to chemical safety
- E-Books: Ergonomics and Psychology Developments in Theory and Practice
- E-Books: HAZOPS Should BE fun-The Stream-Based HAZOP
- E-Books: Safety Health and Environmental Auditing
- E-Books: A Quick Guide to Health and Safety
- E-Books: Occupational Ergonomics A Practical Approach
- E-Books: Job Hazard Analysis A Guide for Voluntary Compliance and Beyond
- E-Books: Electrical Safety of Low Voltage Systems