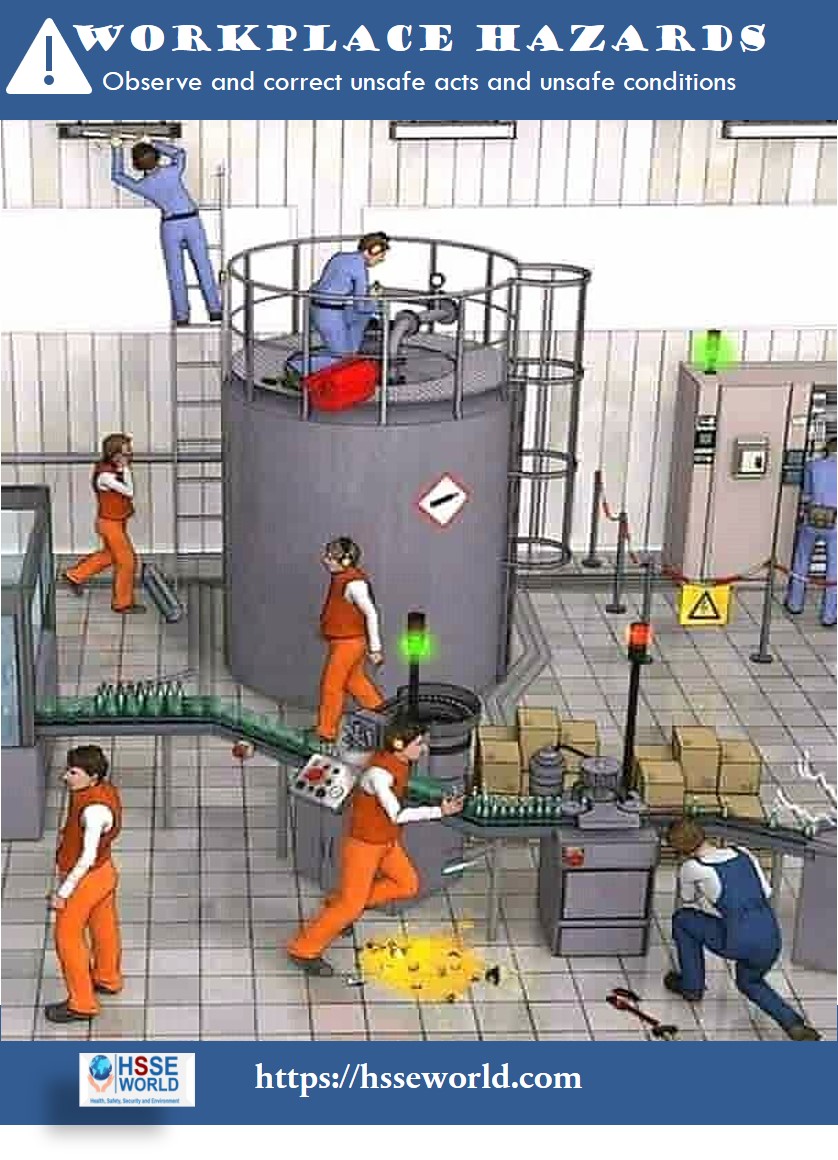
Safety should never be an afterthought; especially in the workplace, as organizational efficiency directly depends on the well-being of employees. Hence, if you want to achieve higher productivity in the workplace, you must make workplace safety an integral part of any organizational culture.
In this post, you will learn about workplace safety, common workplace hazards and accidents, workplace safety strategies, and accident prevention tips.

What is Workplace Safety?
Workplace safety refers to the limitation of elements that can cause harm, accidents, and other negative outcomes in the workplace. It represents a culmination of policies, behaviors, and precautions that work to limit hazards, accidents, and other kinds of harm in a work environment.
More often than not, workplace safety directly affects the productivity and well-being of your workforce, and these directly affect the quality of output of your business. Hence, employers must strive to create a safe environment that offers an acceptable level of risk for all employees.
Also, employees must be quick to identify situations and conditions in the workplace that can jeopardize their safety or expose them to unacceptable risk levels. In the United States of America, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) acts as the regulatory body for workplace safety.
7 Types of Workplace Hazards and How to Prevent Them
Electrical Accident
Electrical accidents are very common in the workplace and they are caused by unprotected exposure to high voltage electrical outlets. ( Read more about high voltage electrical safety). According to the Electrical Safety Foundation International, electrical hazards cause more than 300 deaths and 4,000 injuries in American workplaces every year.
Electrical burns, electrical fires, and electrical shocks are 3 major types of electrical accidents. Electrical shocks occur when bodily contact with electricity causes the current to run through your body and in severe cases, it can lead to heart or respiratory failures.
( learn more: Types of Electrical Injuries).
Many times, electrical burns are aftermaths of electrical shocks and they can be internal or external. Electrical fires occur when un-insulated wiring or broken circuits come in contact with flammable material in the workplace such as cotton and wood shavings.
When workers have to make use of faulty extension cords or work in environments littered with exposed power lines, they are directly at risk of electrical accidents. Such exposure can result in minor to major injuries especially burns, cardiac arrest, and even death (electrocution) in many cases.
Other scenarios that can result in electrical accidents include the following:
- Hidden electrical outlets in the workspace.
- Unsafe equipment or installation.
- Lack of personal protective equipment.
- Poor control of work activities
- Un-insulated electrical wiring
- Lack of training
- Failure to isolate circuits before working
Here are a few things to do when electrical accidents; especially shocks and burns, happen in the workplace.
- Avoid touching the victim with your hands.
- Do not remove any blisters or burnt flesh from the victim’s body.
- Do not rub any ointment on the burns.
Workplace Safety Tips to Prevent Electrical Hazards
To protect your employees and prevent electrical shock accidents in the workplace, employers and employees must take extra care to practice workplace safety habits. Specifically, here are a few precautions you can take:
- Always inspect the working area for uninsulated wires, broken cord, and exposed electrical circuits beforehand.
- Do not make use of faulty electrical equipment at all times.
- Workers must wear personal protective equipment.
- Isolate electrical equipment before working on them.
- Have a prompt system for reporting and documenting electrical shock incidents in the workplace. You can make use of the Formplus Incident Report Form for noticing, reporting, and investigating electrical hazards.
Exposure to Dangerous Chemicals
Toxic chemicals in the workplace can also hamper the safety of employees; especially when they are exposed to these substances without appropriate caution. Chemical exposure can result in a number of effects ranging from cancer and organ failures to death. (Read More E-books-NIOSH pocket guide to-chemical hazards)
There are different toxic chemicals that employees may be exposed to as they complete daily tasks in the workplace. Usually, these chemicals are classified according to the type of harm that they can cause to the body as shown below:
- Corrosives: These are chemicals that can cause irreversible bodily harm such as hydrochloric acid.
- Irritants: Exposure to irritant chemicals can result in reversible inflammation of the contact skin area. Examples of irritant chemicals include strong solvents.
- Teratogens: This class of chemicals can cause birth defects when employees are exposed to them. A popular teratogen in the workplace is thalidomide.
- Sensitizers: A sensitizer, such as an isocyanate, can trigger allergic reactions upon exposure.
- Mutagens: Exposure to this type of chemicals can lead to negative gene mutation and damage to the chromosomes. A good example of this chemical is benzene.
- Carcinogens: A carcinogen is a chemical that can trigger malignant growth in body cells; thereby potentially causing cancer. Asbestos is a common carcinogen.
Employees can be exposed to these chemicals through inhalation, direct or indirect skin contact, ingestion, and injection. Unlike other workplace accidents, the effects of chemical exposures are typically gradual and long-term and their impacts are far-reaching.
Workplace Safety Tips to Prevent Exposure to Dangerous Chemicals
- Wear personal protective equipment while handling chemicals in the workplace.
- Limit individual employees’ exposure to chemicals by creating a work roaster.
- Monitor daily employee safety using the Formplus employee safety review form.
Machinery & Tools Hazard
Employees who work in industries that require the use of machinery and tools such as construction or transportation are at risk of machinery and tools accidents. A report by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration suggests that 12 of the 874 deaths in the construction industry in 2014 resulted from machinery and tools accidents.
In many cases, these accidents are caused by the use of faulty equipment, lack of adequate knowledge, product defects, or negligence of stipulated safety precautions. Common examples of workplace machinery and tools accidents are:
- A burn caused by a faulty heater in the factory.
- Falls from a defective ladder or shaky scaffolding.
- Cuts from broken tools or sharp tool edges.
- Injuries caused by the use of the wrong tool.
- Hearing loss as a result of working in the factory without earmuffs.
- Lacerations or amputations as a result of the use of equipment without safety mechanisms.
- Crush injuries due to machine entanglement.
Workers who are victims of machinery and tools accidents are entitled to some sort of compensation that caters to medical bills and similar expenses. If the accident was caused by a defective product, such an employee may have a product liability claim against the manufacturer (s) of the equipment.
Workplaces Safety Tips to Prevent Machine and Tool Accidents
- Organizations must carry out frequent risk assessments.
- Tools and machinery should be maintained regularly and replaced when due.
- Use the Formplus incident report form to swiftly file reports of any machinery and tools to prevent accidents.
- Appropriate protective equipment must be worn in the workplace.
- Employees must undergo training on how to make use of machinery and tools.
- Safety guards must be fitted into workplace equipment.
( Read More: investing-in-machine-safety).
Workplace Harassment
Workplace harassment is a common problem that can result in an unhealthy working environment, reduced productivity, and toxic behaviors. It encompasses any actions that repeatedly threaten, abuse, ridicule, or discriminate against employee(s) and can have adverse effects on work performance.
Many times, such negative actions are targeted towards specific demography; thus, employees may suffer abuse and discrimination as a result of their social status, gender, race, or physical appearance. Workplace harassment is also known as workplace aggression and it can take several forms including bullying, psychological abuse, and sexual assault.
Behaviors and actions that can be termed “harassing” in the workplace cut across body-shaming, offensive jokes, and slurs such as racist comments, intimidation, and physical assaults. The harasser does not have to be your boss or employer; it can be a co-worker or even someone who has other affiliations with the organization such as a client.
As a victim of workplace harassment, the first thing you may want to do is stand up for yourself and clearly communicate your disapproval of such behavior to your harasser. Also, utilize appropriate complaint channels to report cases of workplace harassment for redress.
How to Prevent Workplace Harassment
- Organizations must take extra care to create and implement anti-harassment policies.
- Educate staff on workplace harassment.
- Use the Formplus workplace harassment form for effective monitoring and reporting of workplace harassment.
Fire Accidents
A fire accident is a very serious danger that can result in loss of life and property in the workplace. A report by the US Bureau of Statistics states that nearly 200 workers die from workplace fires and explosions every year, and more than 5,000 others sustain minor to major injuries. (Read More:E-books-a-guide-to-fire-safety-engineering)
The first step to preventing a fire outbreak in any organization is recognizing potential causes. Here is a list of some of the things you should look out for
- Faulty Electrical Equipment: Electrical fire is one of the most common types of fire accidents in workplaces. An electrical fire can be sudden, widespread in a few minutes, difficult to contain, and very destructive.
- Clutter: Untidy work environments can also result in fire outbreaks. When workspaces are littered with inflammable material and poorly ventilated, it is easy for fire accidents to happen.
- Combustible Materials: Organisations that utilize combustible materials for production must take extra safety precautions when handling them. Failure to do this increases the risk of fire outbreaks.
- Negligence: When employees fail to adhere to safety precautions, such negligence can result in fire accidents.
How to Prevent Workplace Fire Accidents
- Create numerous fire exits in the workplace. Fire exits should complement the size and composition of your building.
- Install fire alarms and extinguishing systems.
- Do not place inflammable materials near ignition sources like circuits and electrical outlets.
- Organize compulsory fire drills regularly.
- Promptly inform your employer about fire hazards using the Formplus incident report form.
- Do not overload power circuits.
Workplace Theft
Workplace theft occurs when an employee illegally obtains cash or non-cash properties from his or her organization. Many times, employees who engage in workplace theft see this as a means of settling scores with their employers or getting back at their employers for poor remuneration or other unfavorable working conditions.
In some other cases, employees feel that engaging in workplace theft will not affect the organization; especially when such action involves obtaining non-cash properties like office equipment, stationery, or office supplies. In other words, these persons view the organization as an anonymous entity that will not suffer significant hurt as a result of their “minor” actions.
As an employer, you may have been a victim of one or more of these types of workplace theft:
- Billing: An employee may inflate the prices of goods and services or present fake invoices for payment.
- Cash Larceny: This occurs when an employee diverts incoming payments for goods and services after such a transaction has been filled in the organization’s books.
- Payroll: Some employees can apply for compensation for work not done such as payments for false overtime.
- Cash Theft: Cash theft is one of the most common types of workplace theft. It involves unlawful obtaining of cash held in the workplace such as stealing money from the company’s safe.
- Expense Reimbursement: When applying for reimbursement, some employees can inflate the actual costs incurred in order to claim more money.
How to Prevent Workplace Theft
- Use the incident report form to report any cases of theft in your organization.
- Create and implement workplace anti-theft policies.
- Organize anti-theft workshops for employees.
- Limit the amount of cash on hand in the workplace.
- Always verify receipts and invoices before making payments.
Workers Existing Health Conditions
Workers with underlying health conditions are more susceptible to certain types of accidents in the workplace such as accidents resulting from chemical exposure. Employers must take care to accurately document the medical history of employees and to also carry out medical examinations before employment.
It is also important for employers to provide conducive and safe working environments for workers as poor working conditions can aggravate pre-existing health conditions in employees. For instance, a worker who is asthmatic may have an attack if he or she is forced to work in an environment that has poor ventilation systems.
Workers with pre-existing health conditions should not be discriminated against; although this has hardly been the case. Many times, pre-existing health conditions affect remuneration such that employees in this demography may earn.
Nevertheless, employees with any underlying illnesses should always inform their employers in order to get the best care even as they go about different tasks in the workplace. In addition, such persons must insist on extra safety measures at work.
How to Protect Workers with Underlying Illnesses in the Workplace
- Implement flexible working hours for workers with pre-existing health conditions.
- Limit the exposure of such employees to workplace hazards such as toxic chemicals.
- Observe additional safety precautions in the workplace.
- Use the Formplus employee complaint form to track and record any safety complaints made by employees.
How to Manage Workplace Accidents
- Proper Orientation/Training
Employees must be duly informed about workplace safety measures and trained on how to maintain workplace safety at all times. As an employer, normalize organizing compulsory safety workshops and training that deal with different aspects of workplace safety for all stakeholders in your organization.
Safety training in the workplace should focus on familiarising employees with different workplace hazards and how to identify, report, and prevent them. Employees should undergo proper training before making use of any equipment in the workplace and they should also observe other safety precautions that can help to prevent accidents.
- Have a Safety Policy Every Employee Must Follow
In line with stipulated guidelines provided by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), your organization must draft and implement a compulsory workplace safety policy for all employees. Every employee must get acquainted with these safety guidelines and adhere to them at all times.
In your workplace safety policy, detail procedures for dealing with emergency situations such as fire outbreaks and workplace violence. Your organization’s safety policy must be reviewed from time to time and every employee must have a copy of this document for future references.
Here is a workplace safety policy template.
- Incident Report
Create an effective system for filing and processing reports on different types of workplace accidents. Employees should make it a point of duty to swiftly report any accidents in the workplace to the management for proper investigation and other necessary actions.
You can set up a manual system for incident reports using paper forms and verbal reporting channels or you can automate the process with the Formplus incident report form. With the Formplus incident report form, you can easily document any injuries, disasters, or accidents in the workplace.
- Safety Team for Standards and Monitoring
More than creating workplace safety policies, organizations must set up in-house regulatory teams that work to ensure adherence to these standard practices. This team can conduct regular safety surveys using the Formplus employee survey form to gather feedback on the effectiveness of safety precautions and other necessary information.
Conclusion
Employees have the right to be safe even as they carry out different tasks in every organization. Hence, every employer must prioritize workplace safety and look after employee protection in order to promote the well-being of all staff in the organization and sundry.
Ensuring safety in the workplace is everyone’s responsibility as a breach of safety has dire consequences. Hence, employees must undergo proper orientation on workplace safety measures and tips while safety monitoring systems should be set up and monitored, accordingly.
Download the photo
More photos:
- What are the Best Practices for Managing Subcontractor Risk
- Photo of the day: 10 Essential Safety Tips for Driving in Hot Weather Conditions
- Photo of the day: best workplace safety tips
- Photo of the day: The Importance of Stop Work Authority in Maintaining Workplace Safety
- Photo of the day: Tomorrow’s Reward for Working Safely Today: Cultivating a Culture of Safety
- Photo of the day: Preventing slips and trips at work
- Photo of the day: Learn the DRSABCD action Plan
- Working with Electricity Electrical Accidents Guide for Electrical Workers
- Photo of the day: Hearing Protection Device Selection
- Photo of the day: If An Earthquake Shakes You-Infographic free
- Fire Safety Posters Free Download
- Photo of the day: First Aid for Electrical Burns-Infographic free
- Infographic: First Aid for Cuts and Scrapes free download
- Photo of The day: Work Safe with Lasers-Laser Safety free
- Photo of the day: Working Safely with chemicals and chemical Management
- Photo of the day: Safe work practices when using MEWPs ( updated)
- Photo of the day: Preventing Common Kitchen Hazards
- Photo of the day: Safe handling of Gas Cylinders and lecture bottles
- Photo of the day: Forklift Stability Triangle
- Photo of the day: Defective Tools Safe Work Practice
- Photo of the day: Lift With Your Legs Not With Your Back
- Photo of the day: First Aid for burns
- Photo of the day: The 7 Principles of HACCP
- Photo of the day: Working Safely with Suspended Loads
- Photo of the day: Heat Stroke First Aid and safety posters
- Photo of the day: Near-Miss Reporting and Posters
- Photo of the day: Ergonomic chair and office chair safety tips
- Photo of the day: Whole Body Vibration
- Photo of the day: Substation Safety Equipment
- Photo of the day: Bypassing Safety Controls Rules
- Photo of the day: Lightning Safety Tips
- Photo of the day: Overhead Power lines Clearance
- Photo of the day: Floor Marking
- Photo of the day: Types of Foot Protection
- Photo of the day: Types of Hand Protection
- Photo of the day: Lockout and Tagout Safety
- Photo of the day: Fall Protection Plans
- Photo of the day: Flood Safety Tips
- Photo of the day: Read All Labels Work safe
- Photo of the day: Run Project safely with Crane Hand Signals
- Photo of the day: Flagman and Traffic control
- Photo of the day: Managing Risks of Exposure to Solvents in the workplace
- Photo of the day: Scissor Lift Safety
- Photo of the day: HSE Bulletin Board
- Photo of the day: Arc-Fault Circuit Interrupters (AFCI)
- Photo of the day: Safe use of ladders and step ladders
- Photo of the day: Concrete Truck Driver Hand Signals
- Photo of the day: Extension Cord Safety Tips
- Photo of the day: Protect your Head
- Photo of the day: choosing the right Anchorage
- Photo of the day: Work-Related Asthma
- Photo of the day: Top FIVE Heavy Equipment Construction Site Safety Tips
- Photo of the day: sun safety in the workplace
- Photo of the day: Cannabis and Impairment in the Workplace
- Photo of the day: Position for safety and comfort-Safety Tips
- Photo of the day: Generator Safety
- Photo of the day: Controlling COVID-19 in the Workplace-Physical Barriers
- Photo of the day: Manual Material handling
- Photo of the day: Personal Protective Equipment last resort
- Photo of the day: WHMIS 2015 – Pictograms
- Photo of the day: Indoor Air Quality
- Photo of the day: Noise in the affected workplace
- Photo of the day: Fatigue at Work
- Photo of the day: Don’t be Driven to Distraction
- Photo of the day: working in heat and Humidex Rating
- How to use Plate Clamps Safely: Safety Moment#34
- Photo of the day: Sitting at work
- Photo of the day: 5 ways to reduce the risk of Slipping and Tripping
- Photo of the day: Preventing the spread of contagious illness
- Photo of the day: Incident Investigations
- Photo of the day: 10 Scaffold Safety Essentials
- Photo of the day: Effective Health and Safety Committees
- Photo of the day: New worker Orientation & Safety Orientation checklist
- Photo of the day: Workplace Inspection
- Photo of the day: musculoskeletal disorders
- Photo of the day: Emergency preparedness in the workplace
- Photo of the day: Mental health in the workplace
- Photo of the day: Trenching Safety Tips That Can Save a Life
- Photo of the day: Dangerous Goods Classes
- Photo of the day: Safety Equipment for Confined Spaces
- Photo of the day: Tips to reduce Heat stress in the workplace
- Photo of the day: hierarchy of controls
- Your steps to chemical safety
- H2S Gas and how to handle its Emergency
- Photo of the day: Importance of Mock drill and Fire Action Emergency Procedure
- Photo of the day: Choosing the Right Face Mask and the difference between a respirator and face mask
- Photo of the day: Confined space safety Precautions
- Breath Safely: The Proper Use of Respiratory Protection
- Photo of the day: Electric shock survival
- Photo of the day: Chemical Spill Emergency Response
- Photo of the day: Construction Site fire Safety
- Photo of the day: Confined Space rescue
- Photo of the day: Conveyors Safety Tips