Photo of the day: Workplace Inspection
7 min readWorkplace inspections are an important prevention tool that can prevent injuries and illnesses and ensure that your health and safety program is working. The goal is to find any unsafe acts or conditions and implement necessary controls.
The photo of today will outline Inspection tips, types of inspection, and hazards to look for during work activities at the workplace to ensure providing a safe workplace free of any hazards.
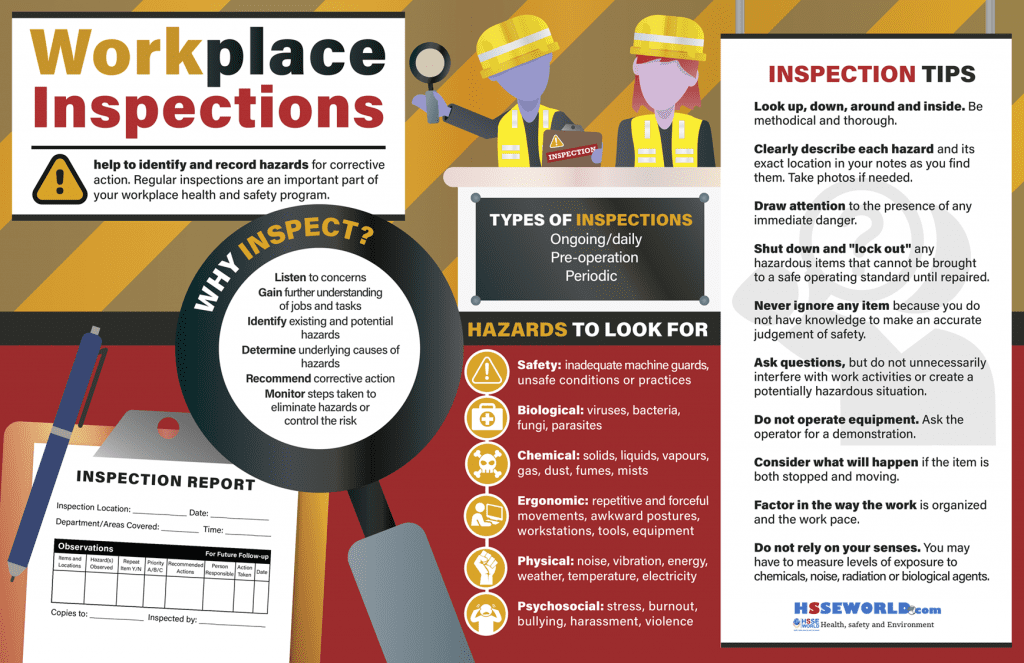
Why are workplace inspections important? Workplace inspections help prevent incidents, injuries, and illnesses. Through an examination of the workplace, inspections help to identify and record hazards for corrective action.
Health and safety committees can help plan, conduct, report, and monitor inspections. Regular workplace inspections are an important part of the overall occupational health and safety program and management system if present.
What is the purpose of inspections?
Workplace inspections allow you to:
- Listen to the concerns of workers and supervisors
- Gain further understanding of jobs and tasks
- Identify existing and potential hazards
- Determine underlying causes of hazards
- Recommend corrective action
- Monitor steps are taken to eliminate hazards or control the risk (i.e. engineering controls, administrative controls, policies, procedures, personal protective equipment)
What should you examine during a workplace inspection?
Every inspection must examine who, what, where, when, and how. Pay particular attention to items that are or are most likely to develop into unsafe or unhealthy conditions because of stress, wear, impact, vibration, heat, corrosion, chemical reaction, or misuse. Include areas where no work is done regularly, such as parking lots, rest areas, office storage areas, and locker rooms.
Look at all workplace elements – the people, the environment, the equipment, and the process. The environment includes such hazards as noise, vibration, lighting, temperature, and ventilation. Equipment includes materials, tools, and apparatus for producing a product or a service. The process involves how the worker interacts with the other elements in a series of tasks or operations.
Who can help me conduct a workplace inspection?
A program for inspecting the entire workplace at least once a month must be developed with the joint health and safety committee (JHSC) or health and safety (H&S) representative. The workplace can be divided into sections, each with its own inspection person or team. Inspections may also be scheduled daily, weekly, monthly, or annually or at other frequencies depending on the nature of the issue, requirements of legislation, and the regulations (for example, a lift truck must be inspected daily ), or as recommended by equipment manufacturers. You can also use your hazard identification system and incident history to help identify areas that may require more frequent inspections. Ideally, inspections should be done on a schedule that will prevent the development of unsafe conditions.
(Read more:https://hsseworld.com/annual-internal-audit-form/).
There are four main types of inspections:
- Formal (Planned) – normally done by using a written checklist and carried out by a team at regular intervals.
- Informal (On the spot) – done by management, supervisors, and JHSC or H&S representatives by observing the area for unsafe acts and conditions, and noting the issues in the daily log or by completing a simple form.
- Specialized inspections – conducted by specialists (for example on boilers, electrical equipment, mechanical or ventilation systems).
- Regulatory – normally consists of inspections required by the OHS regulations. Examples include inspection of fall protection equipment.
Note: The scope of this OHS Guide is to address formal or planned inspections.
An inspection team should include both employee and employer representatives. They should be familiar with the work process and, whenever possible, including members of the JHSC or H&S representative.
Formal or planned inspections should be done using a formal checklist, tailored to the workplace’s needs. Items on the checklist should not be considered permanent as incidents, changes in process, and near misses may result in new items being added to the checklist. A sample checklist is provided as an example.
Identified hazards must be classified, using a hazard classification system; this will ensure that hazards are addressed by rankings. An example is provided at the end of the sample checklist.
As an employer, you must:
- Include the procedures and schedules for inspections in the hazard identification system when a health and safety program is required in the workplace.
- Ensure that the place of employment is inspected at least monthly to identify any risks to employee health and safety.
- Develop a program for the inspection with the JHSC or the H&S representative and share the results of each inspection with the JHSC or the H&S representative.
- Train employees to regularly inspect their machinery, tools, and equipment.
- Ensure that inspection results are recorded and significant findings are acted on.
The steps to follow for a successful inspection include:
- Planning your route and any primary concerns to be observed.
- Observing tasks being done.
- Asking questions, making notes.
- Examining equipment, checking maintenance records.
- Checking that the work area is tidy and that tools have a storage place.
- Looking for what might not be obvious such as fire doors not opening outward or being blocked.
- Establishing clear procedures that identify when and how often to conduct each inspection. Some tasks may require daily or start-of-shift inspections. Record who will do them and who will follow up.
- While the workplace requires monthly inspections, more frequent inspections may be required and a schedule should be established based on the frequency of work, degree of hazard, and a history of incidents or near misses.
- Keeping records of all inspections, findings, recommendations, and follow-up.
- Ensuring the JHSC (or H&S representative) sees the reports and follow-up.
( read more:site-equipment-and-tools-inspection-procedure/).
Download Infographic
Workplace Inspection
More Photos
- Photo of the day: 10 Essential Safety Tips for Driving in Hot Weather Conditions
- Photo of the day: best workplace safety tips
- Photo of the day: The Importance of Stop Work Authority in Maintaining Workplace Safety
- Photo of the day: Tomorrow’s Reward for Working Safely Today: Cultivating a Culture of Safety
- Photo of the day: Preventing slips and trips at work
- Photo of the day: Learn the DRSABCD action Plan
- Working with Electricity Electrical Accidents Guide for Electrical Workers
- Photo of the day: Hearing Protection Device Selection
- Photo of the day: If An Earthquake Shakes You-Infographic free
- Fire Safety Posters Free Download
- Photo of the day: First Aid for Electrical Burns-Infographic free
- Infographic: First Aid for Cuts and Scrapes free download
- Photo of The day: Work Safe with Lasers-Laser Safety free
- Photo of the day: Working Safely with chemicals and chemical Management
- Photo of the day: Safe work practices when using MEWPs ( updated)
- Photo of the day: Preventing Common Kitchen Hazards
- Photo of the day: Safe handling of Gas Cylinders and lecture bottles
- Photo of the day: Forklift Stability Triangle
- Photo of the day: Defective Tools Safe Work Practice
- Photo of the day: Lift With Your Legs Not With Your Back
- Photo of the day: First Aid for burns
- Photo of the day: The 7 Principles of HACCP
- Photo of the day: Working Safely with Suspended Loads
- Photo of the day: Heat Stroke First Aid and safety posters
- Photo of the day: Near-Miss Reporting and Posters
- Photo of the day: Ergonomic chair and office chair safety tips
- Photo of the day: Whole Body Vibration
- Photo of the day: Substation Safety Equipment
- Photo of the day: Bypassing Safety Controls Rules
- Photo of the day: Lightning Safety Tips
- Photo of the day: Overhead Power lines Clearance
- Photo of the day: Floor Marking
- Photo of the day: Types of Foot Protection
- Photo of the day: Types of Hand Protection
- Photo of the day: Lockout and Tagout Safety
- Photo of the day: Fall Protection Plans
- Photo of the day: Flood Safety Tips
- Photo of the day: Read All Labels Work safe
- Photo of the day: Run Project safely with Crane Hand Signals
- Photo of the day: Flagman and Traffic control
- Photo of the day: Managing Risks of Exposure to Solvents in the workplace
- Photo of the day: Scissor Lift Safety
- Photo of the day: HSE Bulletin Board
- Photo of the day: Arc-Fault Circuit Interrupters (AFCI)
- Photo of the day: Safe use of ladders and step ladders
- Photo of the day: Concrete Truck Driver Hand Signals
- Photo of the day: Extension Cord Safety Tips
- Photo of the day: Protect your Head
- Photo of the day: choosing the right Anchorage
- Photo of the day: Work-Related Asthma
- Photo of the day: Top FIVE Heavy Equipment Construction Site Safety Tips
- Photo of the day: sun safety in the workplace
- Photo of the day: Cannabis and Impairment in the Workplace
- Photo of the day: Position for safety and comfort-Safety Tips
- Photo of the day: Generator Safety
- Photo of the day: Controlling COVID-19 in the Workplace-Physical Barriers
- Photo of the day: Manual Material handling
- Photo of the day: Personal Protective Equipment last resort
- Photo of the day: WHMIS 2015 – Pictograms
- Photo of the day: Indoor Air Quality
- Photo of the day: Noise in the affected workplace
- Photo of the day: Fatigue at Work
- Photo of the day: Don’t be Driven to Distraction
- Photo of the day: working in heat and Humidex Rating
- How to use Plate Clamps Safely: Safety Moment#34
- Photo of the day: Sitting at work
- Photo of the day: 5 ways to reduce the risk of Slipping and Tripping
- Photo of the day: Preventing the spread of contagious illness
- Photo of the day: Incident Investigations
- Photo of the day: 10 Scaffold Safety Essentials
- Photo of the day: Effective Health and Safety Committees
- Photo of the day: New worker Orientation & Safety Orientation checklist
- Photo of the day: Workplace Inspection
- Photo of the day: musculoskeletal disorders
- Photo of the day: Emergency preparedness in the workplace
- Photo of the day: Mental health in the workplace
- Photo of the day: Trenching Safety Tips That Can Save a Life
- Photo of the day: Dangerous Goods Classes
- Photo of the day: Safety Equipment for Confined Spaces
- Photo of the day: Tips to reduce Heat stress in the workplace
- Photo of the day: hierarchy of controls
- Your steps to chemical safety
- H2S Gas and how to handle its Emergency
- Photo of the day: Importance of Mock drill and Fire Action Emergency Procedure
- Photo of the day: Choosing the Right Face Mask and the difference between a respirator and face mask
- Photo of the day: Confined space safety Precautions
- Breath Safely: The Proper Use of Respiratory Protection
- Photo of the day: Electric shock survival
- Photo of the day: Chemical Spill Emergency Response
- Photo of the day: Construction Site fire Safety
- Photo of the day: Confined Space rescue



