Many workers are unaware of the potential electrical hazards in their work environment, which only increases their risks. Engineers, electricians, construction workers, and other professionals work directly with or near electricity, such as overhead power lines, cable harnesses, and circuit assemblies. Others, such as factory, office, and retail workers, are often exposed indirectly to electrical hazards through faulty equipment or over-burdened extension cords. Accidental contact with electrical currents can cause electrical burns, electrical shock, electrocution, fires, and explosions. Electrical burns injuries can damage the body tissue or internal organs when a person comes into direct contact with an electrical current. It accounts for 1000 deaths yearly in the United States, with a mortality rate of 3-15%. If you are a worker at risk of electrical shock and burns or a parent with a child at home, the Photo of today will teach you how to treat and prevent electrical burns.
Also Read Minor and Severe Cuts: Workplace First Aid Basics
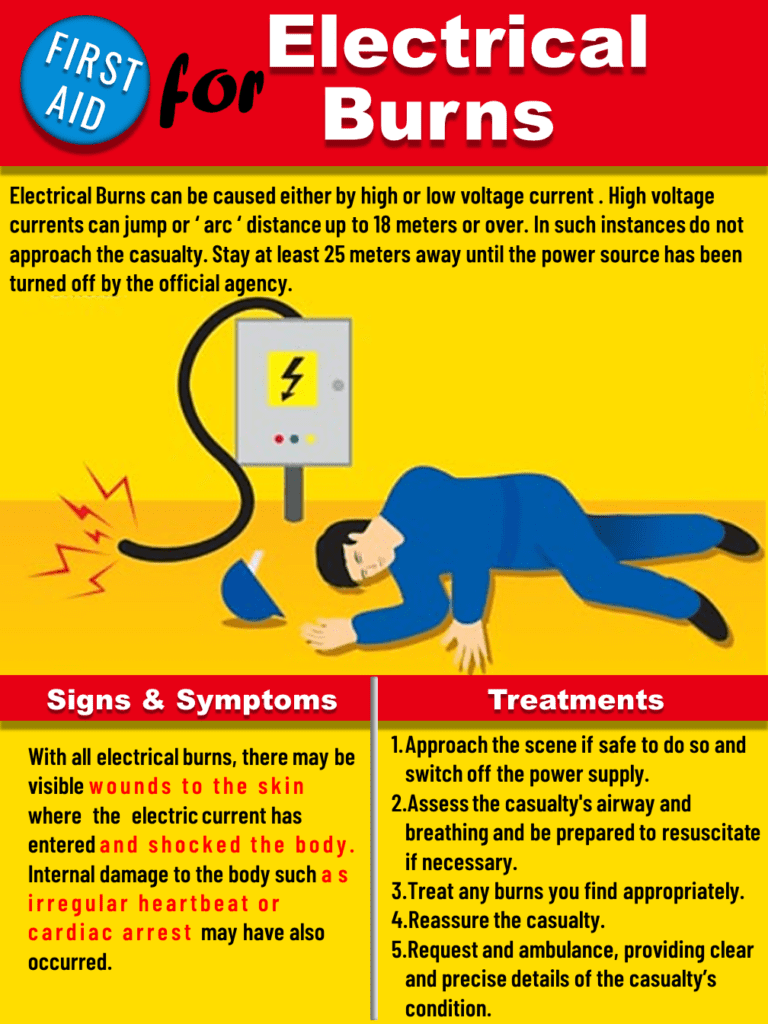
What are Electrical Burns?
Electrical burns are skin burn that happens when the electricity comes in contact with the body’s surface. It may be caused by several sources of electric sources such as lightning strikes, stun guns, and contact with electrical appliances and household currents.
When electricity comes in contact with your skin, it can travel through your body. When this happens, the electricity can damage tissues and organs. This damage can be mild or severe and can even cause death. Organs that are commonly damaged include the following:
- Heart: People can get abnormal heart rhythms. Their heart can also suddenly stop beating, called “cardiac arrest.”
- Kidneys: – The kidneys can stop working normally.
- Bones and muscles: If the muscles are severely injured, substances from inside damaged muscle cells can leak into the blood.
- Nervous system: People can pass out, have muscle weakness, or have eye or ear damage.
Also Read: First aid requirements at construction site
What Are the 3 Types of Electrical Burns?
There are three types of electrical injuries. These are:
1. Electrical burns – This can result when someone touches electrical wiring or equipment used or maintained improperly. It often occurs on the hands. Electrical burns are one of the most severe injuries you can receive. Therefore, they need to be given immediate attention.
2. Arc-blasts – This electric burn occurs when powerful, high-amperage currents arc through the air. This is often caused by equipment failure due to fatigue.
3. Thermal burns – This type of burn (thermal injuries) may result if an explosion occurs or when electricity ignites an explosive material in the air. The ignition can result from the buildup of combustible vapors, gasses, or dust.
Also Read: Types of electrical injuries
What Are the Categories of Electrical Burns?
Burns are classified into three categories, with increasing seriousness.
- First Degree Burn – It affects only the epidermis or outer layer of the skin. This burn causes mild redness, swelling, and pain.
- Second Degree Burn – It affects both the upper layer of the skin and the skin underneath it. Some specific symptoms of this burn include redness, swelling, pain, and blistering.
- Third-Degree Burn – This is the most severe type of burn that destroys the deep layers of the skin. This can lead to numb skin and white or blackened skin.
First Aid for an Electrical Burns:
The first step to take when a person is in contact with an electrical source is to call 911 or other emergency services. For minor or mild burns, follow these first aid steps. If symptoms persist, consult your physician or head to the nearest hospital with an emergency department.
1. Do not touch the electrical burn patient with your hands.
2. Unplug the appliance or turn off the main power source.
3. If you cannot turn the power off, try to remove the person from the source of electricity. Do this safely by standing on a dry surface or using a dry wooden object to push the patient away from the source of electricity.
4. When it is safe, check if the person is conscious and breathing. Then, gently touch and talk to the person.
5. Check whether the person responds to touch or is being talked to after separating them from the electrical source. If the electrified person is not responding, start CPR immediately.
6. If the victim has a burn, remove any clothing that comes off easily and rinse the burn in cool water until the pain reduces. Then, give first Aid for burns.
7. If the person shows any signs of electrical shock, lay them down, with the head slightly lower than the chest and the legs elevated.
8. Stay with the electric burn victim until medical help arrives and watch for signs of infection.
Also, Read: E-Books: Electric Safety Practice and Standards
Download
Before you Leave do not Miss out free Download of the Infographic
Photo of the day: First Aid for Electrical Burns-Infographic
More Photos
- What are the Best Practices for Managing Subcontractor Risk
- Photo of the day: 10 Essential Safety Tips for Driving in Hot Weather Conditions
- Photo of the day: best workplace safety tips
- Photo of the day: The Importance of Stop Work Authority in Maintaining Workplace Safety
- Photo of the day: Tomorrow’s Reward for Working Safely Today: Cultivating a Culture of Safety
- Photo of the day: Preventing slips and trips at work
- Photo of the day: Learn the DRSABCD action Plan
- Working with Electricity Electrical Accidents Guide for Electrical Workers
- Photo of the day: Hearing Protection Device Selection
- Photo of the day: If An Earthquake Shakes You-Infographic free
- Fire Safety Posters Free Download
- Photo of the day: First Aid for Electrical Burns-Infographic free
- Infographic: First Aid for Cuts and Scrapes free download
- Photo of The day: Work Safe with Lasers-Laser Safety free
- Photo of the day: Working Safely with chemicals and chemical Management
- Photo of the day: Safe work practices when using MEWPs ( updated)
- Photo of the day: Preventing Common Kitchen Hazards
- Photo of the day: Safe handling of Gas Cylinders and lecture bottles
- Photo of the day: Forklift Stability Triangle
- Photo of the day: Defective Tools Safe Work Practice
- Photo of the day: Lift With Your Legs Not With Your Back
- Photo of the day: First Aid for burns
- Photo of the day: The 7 Principles of HACCP
- Photo of the day: Working Safely with Suspended Loads
- Photo of the day: Heat Stroke First Aid and safety posters
- Photo of the day: Near-Miss Reporting and Posters
- Photo of the day: Ergonomic chair and office chair safety tips
- Photo of the day: Whole Body Vibration
- Photo of the day: Substation Safety Equipment
- Photo of the day: Bypassing Safety Controls Rules
- Photo of the day: Lightning Safety Tips
- Photo of the day: Overhead Power lines Clearance
- Photo of the day: Floor Marking
- Photo of the day: Types of Foot Protection
- Photo of the day: Types of Hand Protection
- Photo of the day: Lockout and Tagout Safety
- Photo of the day: Fall Protection Plans
- Photo of the day: Flood Safety Tips
- Photo of the day: Read All Labels Work safe
- Photo of the day: Run Project safely with Crane Hand Signals
- Photo of the day: Flagman and Traffic control
- Photo of the day: Managing Risks of Exposure to Solvents in the workplace
- Photo of the day: Scissor Lift Safety
- Photo of the day: HSE Bulletin Board
- Photo of the day: Arc-Fault Circuit Interrupters (AFCI)
- Photo of the day: Safe use of ladders and step ladders
- Photo of the day: Concrete Truck Driver Hand Signals
- Photo of the day: Extension Cord Safety Tips
- Photo of the day: Protect your Head
- Photo of the day: choosing the right Anchorage
- Photo of the day: Work-Related Asthma
- Photo of the day: Top FIVE Heavy Equipment Construction Site Safety Tips
- Photo of the day: sun safety in the workplace
- Photo of the day: Cannabis and Impairment in the Workplace
- Photo of the day: Position for safety and comfort-Safety Tips
- Photo of the day: Generator Safety
- Photo of the day: Controlling COVID-19 in the Workplace-Physical Barriers
- Photo of the day: Manual Material handling
- Photo of the day: Personal Protective Equipment last resort
- Photo of the day: WHMIS 2015 – Pictograms
- Photo of the day: Indoor Air Quality
- Photo of the day: Noise in the affected workplace
- Photo of the day: Fatigue at Work
- Photo of the day: Don’t be Driven to Distraction
- Photo of the day: working in heat and Humidex Rating
- How to use Plate Clamps Safely: Safety Moment#34
- Photo of the day: Sitting at work
- Photo of the day: 5 ways to reduce the risk of Slipping and Tripping
- Photo of the day: Preventing the spread of contagious illness
- Photo of the day: Incident Investigations
- Photo of the day: 10 Scaffold Safety Essentials
- Photo of the day: Effective Health and Safety Committees
- Photo of the day: New worker Orientation & Safety Orientation checklist
- Photo of the day: Workplace Inspection
- Photo of the day: musculoskeletal disorders
- Photo of the day: Emergency preparedness in the workplace
- Photo of the day: Mental health in the workplace
- Photo of the day: Trenching Safety Tips That Can Save a Life
- Photo of the day: Dangerous Goods Classes
- Photo of the day: Safety Equipment for Confined Spaces
- Photo of the day: Tips to reduce Heat stress in the workplace
- Photo of the day: hierarchy of controls
- Your steps to chemical safety
- H2S Gas and how to handle its Emergency
- Photo of the day: Importance of Mock drill and Fire Action Emergency Procedure
- Photo of the day: Choosing the Right Face Mask and the difference between a respirator and face mask
- Photo of the day: Confined space safety Precautions
- Breath Safely: The Proper Use of Respiratory Protection
- Photo of the day: Electric shock survival
- Photo of the day: Chemical Spill Emergency Response
- Photo of the day: Construction Site fire Safety
For Many Safety Resources please visit SAFETY BAG




