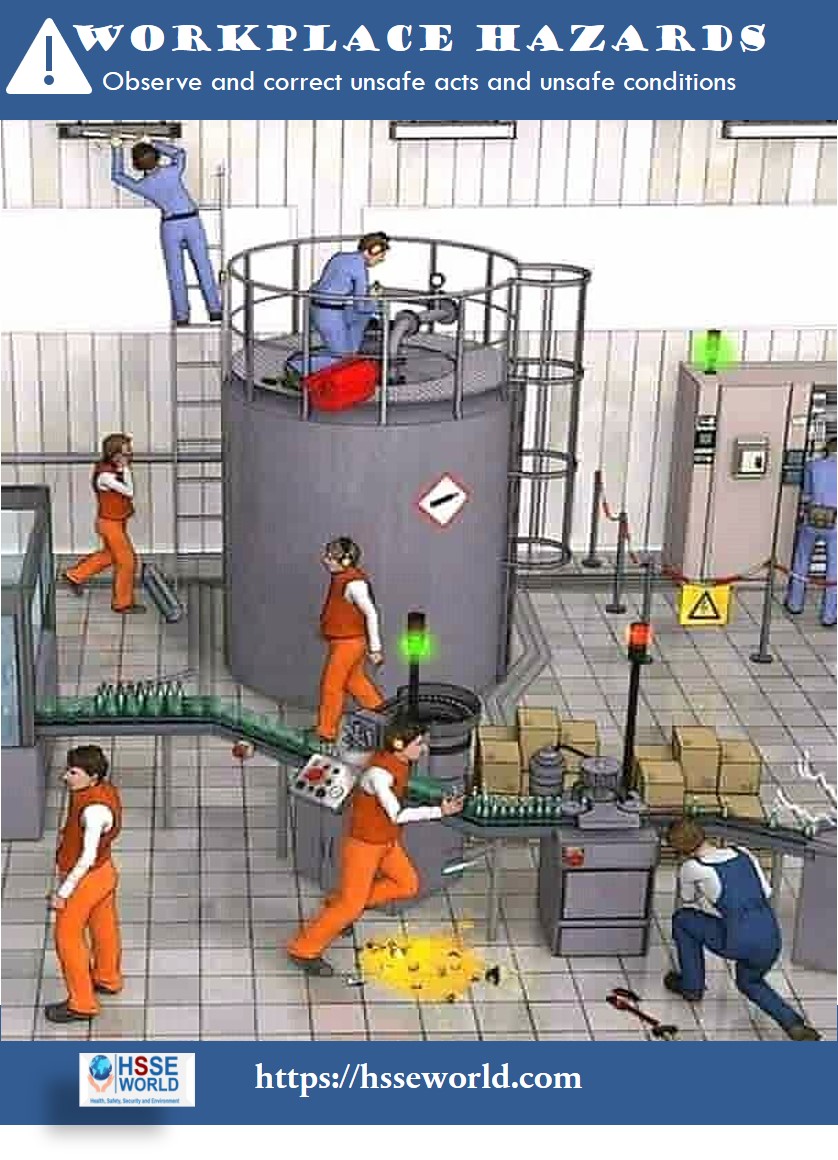
To ensure that the workplace is safe to conduct work activities, it is sometimes necessary to bypass a safety controls system. The risks that are associated with bypassing a system must be thoroughly evaluated to ensure that all necessary precautions are taken. When the need to bypass the system recedes, the system is restored to its normal operational status.
- Example: Defining a bypass operation to turn off a fire alarm
Pipeline workers in Company ABC must occasionally turn off a fire alarm. To comply with safety standards, Company ABC creates a bypass operation record for this activity. - Creating bypass operation records
A bypass operation temporarily stops a component of a system or stops the entire system. When you create a bypass operation record, you describe the reasons for the bypass operation and include the actions to take for that bypass operation. You also secure the approvals and reviews for the bypass operation.
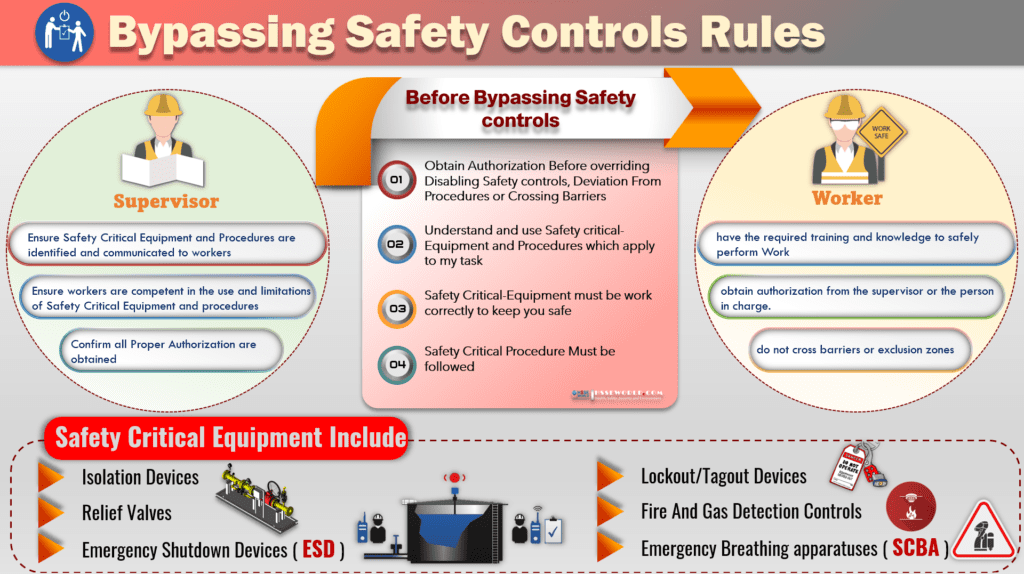
In the photo of today, we will outline one of nine live-saving rules ” Bypass Safety controls” and you will be familiar with :
- Bypass Safety Controls Definition
- The Actions Required before taking the bypass safety controls.
- Supervisor and workers’ Roles and Responsibilities.
- Case study and example of Violations.
Also Read: What are The Types of Valves?
What is the Meaning of Bypass Safety Controls?
A bypass safety control is defined as an operation / A process to inhibit temporarily stops the functioning of a component of a system or stops the entire system. Also bypass operation record/ A process to describe the reasons for the bypass operation, the scope, and the actions to take that related to the bypass operation.
Bypass Operation aims and objectives
- It is sometimes necessary to bypass a safety control system to ensure that the workplace is safe to conduct work activities,
- To evaluate and assess the risks and hazards that are inherent in bypassing a system before you proceed with the bypass operation and the appropriate precautions must be in place.
- It is sometimes necessary to bypass operations to be reviewed and approved multiple times because of the high risks that might be involved with some of the tasks.
- When a bypass is removed and the system is returned to operation, the system must be verified to ensure that normal functioning is restored.
Bypass Operations and Workflow Process
- You can create workflow processes that reflect your business processes.
- A workflow process defines the actions and the notifications that can occur at different points in a business process.
- You can manage the movement of a record through a process from start to finish.
- You can instruct individuals to act on records, ensure that individuals act in a timely manner, and ensure that an audit trail exists for each record and process.
- You use the Workflow application to plan, design, build, test, implement, and manage workflow processes.
Example
Bypass operations are conducted on safety-related systems such as emergency shutdown systems, fire and gas systems, and alarm systems.
Methodology
- When you create a bypass operation record, you describe the reasons for the bypass operation
- You include the actions to take for that bypass operation
- You can create a service level agreement and apply it to a bypass operation to ensure that the level of service complies with the agreement.
- You secure the approvals and reviews for the bypass operation
- You obtain work authorization valid with a work permit before starting the task.
- obtain authorization and confirm the following before starting the task
- Disabling or overriding safety equipment
- Deviating from procedures
- Crossing barriers
- confirm understanding and using safety-critical equipment and procedures which apply to the task.
- Safety Critical-Equipment must be working correctly to keep you safe
- Safety-Critical Procedure Must be followed
Examples of Safety-Critical Equipment Include:
- Isolation Devices
- Relief valves
- Emergency Shutdown Devices ( ESD)
- Fire and gas detection controls
- Lockout/Tagout Devices
- Emergency Breathing Apparatus ( SCBA)
- In-Vehicle Monitoring System
- Electronic Logging Device ( ELD )
- Also Read: Photo of the day: Lockout and Tagout Safety
- Also Read: What are The Types of Valves?
Note: Drug and alcohol tests and procedures are defined as safety-critical equipment
Supervisor Responsibilities:
- Ensure Safety Critical Equipment and Procedures are identified and communicated to workers
- Ensure workers are competent in the use and limitations of Safety-Critical Equipment and procedures
- Confirm all Proper Authorization are obtained
Workers Responsibilities:
- have the required training and knowledge to safely perform Work
- Obtain authorization from the supervisor or the person in charge to override or disable a safety-critical Control.
- Stop work and notify his supervisor if a procedural deviation is required.
- Do not cross barriers or exclusion zones.
Case Study and Example of violations:
Example of Violations:
- Safety-Critical Procedures are not followed.
- Intentionally exceeding safe operating design limits for process equipment
- An ESD is bypassed without Authorization.
- someone else’s lock is removed without Authorization.
- Gas or fire detection is bypassed without Authorization.
- Gas Detection is not worn or is not turned on as per the work permit, hazard assessment, or work procedures.
- Gas detection alarms are ignored.
- Emergency SCBA is used for routine work.
- Tampering with the in-Vehicle monitoring system
- Defeating a drug or alcohol test.
- A barrier or exclusion zone is ignored.
know and download the Different Types of Work permits
Case Study: Gas release from Shut Down Valve (SDV) Grease Injector Fitting
CAUSE & CONSEQUENCE
- Uncontrolled release of flammable gas or liquid
CONTRIBUTING FACTOR
- Communication
DESCRIPTION OF PROCESS
The 3rd stage compression system comprises 2x 100% trains designed to handle 85.3 MMSCFD of gas.
DESCRIPTION OF INCIDENT
During routine plant maintenance routine function testing of SDV, the central control room informed the instrument technician that the valve had not met its function stroke limits. Valve has been in service since 1992.
Upon investigation, an instrument technician heard audible noise coming from the grease injector fitting on the valve stem. The system was then shut down and isolated for further examination. The valve was removed from service and sent to the vendor to simulate the exact site process test conditions.
During the test the “official leakage rate” was recorded from the grease injector fitting, which indicated failure of the lower stem seal, allowing gas to pressurize behind the grease injector fitting.
The valve was then stripped down and the valve components were found to be in good condition. However, closer inspection indicated that the lower stem seal had ‘collapsed’ and the grease injector NRV check-valve exhibited corrosion on the check-valve seating faces.
A full engineering report was compiled by the vendor, which indicated the root cause as being “injection of grease in a reverse flow direction, causing the lower seal lip seal to collapse”. Secondary component failure of the grease injector fitting found “Corrosion on the check valve seating faces, probably due to the length of time in service, and the environment location of the valve”.
Post Incident – ALL valves in hydrocarbon service were inspected (visual & FLIR Camera) and checked for signs of leakage through injector fittings.
GOOD PRACTICE GUIDANCE
The valve had historically been lubricated with grease through the stem injector fitting to aid the functioning performance of the valve. This fitting had been wrongly assumed to be a grease injector fitting. In fact, its purpose is a stem sealant injector fitting (where the valve is injected with sealant in the event of a lower stem seal failure). Therefore, greasing the cavity between the upper and lower stem seal has caused the collapse of the lower stem lip seal, causing gas to migrate up to the injector fitting.
Stop all greasing in valve stem seal cavities and plug injector ports. (Ensuring plugs are compatible material with valves).
Determine an appropriate course of action to complete a visual survey of gas hydrocarbon system valves greater than 2” this inspection should determine the following:
- Confirm the existence of sealant injector fittings.
- Confirm the presence of leaks at these fittings via FLIR camera inspection.
- Report the presence of leaks to allow each site to assess the suitability for continued use. (As per the requirements of companies weeps, seeps & leaks procedure). Maintain valve register for injector fitting installed. This register should then be uploaded into your maintenance management system.
Download the photo
Now you can download the Infographic ” Bypass Safety Controls Rues ” and post it at the workplace to communicate with everyone to be familiar with the Methodology of Bypassing the Critical Safety Equipment and their roles and Responsibilities
Bypass Safety Controls Rules
More photos:
- What are the Best Practices for Managing Subcontractor Risk
- Photo of the day: 10 Essential Safety Tips for Driving in Hot Weather Conditions
- Photo of the day: best workplace safety tips
- Photo of the day: The Importance of Stop Work Authority in Maintaining Workplace Safety
- Photo of the day: Tomorrow’s Reward for Working Safely Today: Cultivating a Culture of Safety
- Photo of the day: Preventing slips and trips at work
- Photo of the day: Learn the DRSABCD action Plan
- Working with Electricity Electrical Accidents Guide for Electrical Workers
- Photo of the day: Hearing Protection Device Selection
- Photo of the day: If An Earthquake Shakes You-Infographic free
- Fire Safety Posters Free Download
- Photo of the day: First Aid for Electrical Burns-Infographic free
- Infographic: First Aid for Cuts and Scrapes free download
- Photo of The day: Work Safe with Lasers-Laser Safety free
- Photo of the day: Working Safely with chemicals and chemical Management
- Photo of the day: Safe work practices when using MEWPs ( updated)
- Photo of the day: Preventing Common Kitchen Hazards
- Photo of the day: Safe handling of Gas Cylinders and lecture bottles
- Photo of the day: Forklift Stability Triangle
- Photo of the day: Defective Tools Safe Work Practice
- Photo of the day: Lift With Your Legs Not With Your Back
- Photo of the day: First Aid for burns
- Photo of the day: The 7 Principles of HACCP
- Photo of the day: Working Safely with Suspended Loads
- Photo of the day: Heat Stroke First Aid and safety posters
- Photo of the day: Near-Miss Reporting and Posters
- Photo of the day: Ergonomic chair and office chair safety tips
- Photo of the day: Whole Body Vibration
- Photo of the day: Substation Safety Equipment
- Photo of the day: Bypassing Safety Controls Rules
- Photo of the day: Lightning Safety Tips
- Photo of the day: Overhead Power lines Clearance
- Photo of the day: Floor Marking
- Photo of the day: Types of Foot Protection
- Photo of the day: Types of Hand Protection
- Photo of the day: Lockout and Tagout Safety
- Photo of the day: Fall Protection Plans
- Photo of the day: Flood Safety Tips
- Photo of the day: Read All Labels Work safe
- Photo of the day: Run Project safely with Crane Hand Signals
- Photo of the day: Flagman and Traffic control
- Photo of the day: Managing Risks of Exposure to Solvents in the workplace
- Photo of the day: Scissor Lift Safety
- Photo of the day: HSE Bulletin Board
- Photo of the day: Arc-Fault Circuit Interrupters (AFCI)
- Photo of the day: Safe use of ladders and step ladders
- Photo of the day: Concrete Truck Driver Hand Signals
- Photo of the day: Extension Cord Safety Tips
- Photo of the day: Protect your Head
- Photo of the day: choosing the right Anchorage
- Photo of the day: Work-Related Asthma
- Photo of the day: Top FIVE Heavy Equipment Construction Site Safety Tips
- Photo of the day: sun safety in the workplace
- Photo of the day: Cannabis and Impairment in the Workplace
- Photo of the day: Position for safety and comfort-Safety Tips
- Photo of the day: Generator Safety
- Photo of the day: Controlling COVID-19 in the Workplace-Physical Barriers
- Photo of the day: Manual Material handling
- Photo of the day: Personal Protective Equipment last resort
- Photo of the day: WHMIS 2015 – Pictograms
- Photo of the day: Indoor Air Quality
- Photo of the day: Noise in the affected workplace
- Photo of the day: Fatigue at Work
- Photo of the day: Don’t be Driven to Distraction
- Photo of the day: working in heat and Humidex Rating
- How to use Plate Clamps Safely: Safety Moment#34
- Photo of the day: Sitting at work
- Photo of the day: 5 ways to reduce the risk of Slipping and Tripping
- Photo of the day: Preventing the spread of contagious illness
- Photo of the day: Incident Investigations
- Photo of the day: 10 Scaffold Safety Essentials
- Photo of the day: Effective Health and Safety Committees
- Photo of the day: New worker Orientation & Safety Orientation checklist
- Photo of the day: Workplace Inspection
- Photo of the day: musculoskeletal disorders
- Photo of the day: Emergency preparedness in the workplace
- Photo of the day: Mental health in the workplace
- Photo of the day: Trenching Safety Tips That Can Save a Life
- Photo of the day: Dangerous Goods Classes
- Photo of the day: Safety Equipment for Confined Spaces
- Photo of the day: Tips to reduce Heat stress in the workplace
- Photo of the day: hierarchy of controls
- Your steps to chemical safety
- H2S Gas and how to handle its Emergency
- Photo of the day: Importance of Mock drill and Fire Action Emergency Procedure
- Photo of the day: Choosing the Right Face Mask and the difference between a respirator and face mask
- Photo of the day: Confined space safety Precautions
- Breath Safely: The Proper Use of Respiratory Protection
- Photo of the day: Electric shock survival
- Photo of the day: Chemical Spill Emergency Response
- Photo of the day: Construction Site fire Safety
- Photo of the day: Confined Space rescue
- Photo of the day: Conveyors Safety Tips