According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, most of the workers in selected occupations who suffered impact injuries to the feet were not wearing protective footwear or have any type of foot Protection. Furthermore, most employers did not require their workers to wear safety shoes. The typical foot injury was caused by objects falling less than four feet and the average weight of the object was about 65 lb. Most workers were injured while performing their normal job activities at their work sites.
1910.136(a) – General requirements. The employer shall ensure that each affected employee uses protective footwear when working in areas where there is a danger of foot injuries due to falling or rolling objects, or objects piercing the sole, and where such employee’s feet are exposed to electrical hazards.
In the Photo of today, you will be familiar with Different types of foot protection and how to select the proper type of safety shoes that are proper for workplace hazards.
Feet Don’t Fail Me Now! Foot Safety in the Workplace

When Must Foot Protection be Worn?
It is the employer’s responsibility to determine which of their employees, if any, are exposed to a foot injury hazard. To accomplish this employers are required to contact a hazard assessment to identify potential health and physical hazards. Examples of physical hazards that may injure feet include areas where:
- there may be heavy, rolling objects (barrels, pipes, or tools);
- there are objects that may fall;
- sharp objects may pierce the sole of a shoe (nails, spikes, or sharp scrap metal);
- there may be hazardous chemicals that can slash onto feet or the floor;
- there are slippery surfaces;
- there may be exposed to high temperatures (such as molten metal);
- there is exposure to electrical hazards. If there is the possibility an employee’s feet may be exposed to electrical hazards, then non-conductive footwear should be worn. But, if there is the possibility of exposure to static electricity, then wearing conductive footwear is appropriate.
What to do about Foot Hazards
When foot injury hazards are identified the first option is to eliminate them by redesigning equipment, the process, or the facility. If the hazards cannot be eliminated, they should be guarded to prevent access. If they cannot be guarded, administrative rules or procedures can be used to minimize exposure to the hazard. The last line of defense is foot protection.
Identifying a foot injury hazard does not mean that employees exposed to the hazard are required to wear foot protection at all times. Foot protection must only be worn while an employee is exposed to the hazard. If there are times when the employee is not exposed to the hazard, OSHA does not require foot protection. Whether foot protection is to be worn when not required by OSHA is a matter of employment conditions established by the employer or by a union contract.
OSHA 1910 Subpart I Appendix B identifies some occupations for which foot protection should be routinely used. OSHA notes that this is not a complete list:
- shipping and receiving clerks
- stock clerks
- carpenters
- electricians
- machinists
- mechanics and repairers
- plumbers and pipefitters
- structural metal workers
- assemblers
- drywall installers and lathers
- packers, wrappers, and craters
- punch and stamping press operators
- sawyers
- welders
- laborers
- freight handlers
- gardeners and grounds-keepers
- timber cutting and logging workers
- stock handlers
- warehouse laborers
What Type of Foot Protection is Needed?
Different footwear protects in different ways. Check the product’s labeling, or consults the manufacturer, to make sure the footwear will protect the user from the hazards they face. Foot and leg protection choices include the following:
- Leggings are used to protect the lower legs and feet. They are used in situations such when there are welding sparks or the potential for splashes from molten metal. Leggings are typically equipped with safety snaps that allow them to be quickly removed.
- Metatarsal guards are strapped onto the outside of the shoes to protect the instep area from impact and compression.
- Toe guards fit over the toes of regular shoes. They protect the toes from impact and compression hazards.
- Safety shoes have impact-resistant toes and heat-resistant soles. Some safety shoes include metal insoles to protect against punctures. When workers are in areas with potentially explosive atmospheres, safety shoes may be electrically conductive to prevent the buildup of static electricity. In areas where there is exposure to electrical power, safety shoes will be non-conductive, providing protection against electrical shock and burns.
- Special purpose safety shoes – there are a variety of safety shoes designed for specific industries. Here are two examples:
- Cork boots, sometimes called “caulk boots” are used in logging. The soles of corks are covered with small spikes that provide traction when walking on logs.
- Foundry shoes provide insulation against the extreme heat of the molten metal. In addition, foundry shoes are designed to keep the hot metal from lodging in shoe eyelets, tongues or other shoe parts. They are snug-fitting leather shoes that have leather or rubber soles, rubber heels, and built-in safety toes.
Photo of the day: Why is PPE important?
How to Choose Your Shoes
Footwear must be chosen based on the hazards at your site. For example, if you work in a place where you may be at risk of falling objects, choosing a boot based on ankle support isn’t addressing the appropriate risk. Steel-toe work boots are great and traditional protection for several hazards on many different work sites, but are they the right choice for you? Taking the extra time to make sure you know just what you need could make a world of difference.
ASTM F2413, Standard Specification for Performance Requirements for Protective (Safety) Toe Cap Footwear, covers minimum requirements for the design, performance, testing, and classification of protective footwear. Footwear certified as meeting ASTM F2413 must first meet the requirements for impact and compression resistance. Then the requirements of additional sections such as metatarsal protection, conductive protection, electric hazard resistance, static dissipative protection, and protection against punctures can be met.
Here are some of the most frequent potential hazards that require foot PPE. Take a look and see which shoes are made with those hazards in mind. You can also use our safety shoe selection guide to help identify shoes for your work needs.
Electrical Hazards
Electrical hazard boots are an essential piece of PPE for anyone working around electricity. This could be an electrical worker or someone who works around circuits or high voltage machinery. This footwear is manufactured with non-conductive, electrical shock-resistant soles and heels. These kinds of shoes prevent the worker from completing an electrical circuit; this can reduce the chance of electrocution.
Explosives
If you work around explosives or other highly reactive or flammable substances, you will likely need electrically conductive shoes. Electrically conductive work footwear helps prevent the buildup of static electricity on the worker. Without this precaution, static buildup on your body could easily generate a spark that could cause a fire or explosion. Silk, wool, and nylon socks should not be worn in this type of work environment or with this type of shoe, as those materials are more likely to produce static as well.
Chainsaws
Working with chainsaws, or any other rotating blades make protective footwear absolutely necessary. Cut-resistant chainsaw boots (and other cut-resistant clothing) can prevent serious injuries in the face of an accident involving a chainsaw. These are made from specific materials that create a protective barrier from spinning blades.
Falling Objects
If you are at risk of falling items, you will surely want safety toe boots. These are boots that have a capping over the toe area for protection. These toe cappings were traditionally made of steel, hence steel-toed boots. However, now they are also available in composite materials.
Sharp Objects
Sharp objects on the floor pose a workplace hazard. Sharp objects, like nails or screws, can puncture the soles of regular shoes and injure your foot. Puncture-resistant footwear includes steel or composite plate positioned within the midsole to protect from the dangers of stepping on sharp and jagged objects.
Rolling Objects or Machines
Some work footwear has additional protection along the metatarsal region (the top of your foot). If you have ever dropped anything on the top of your foot, you know how much it can hurt. Metatarsal boots are good for work environments where rolling objects or machines present a risk. Any job that involves heavy machinery, heavy loads, or dangerous conditions can require the use of metatarsal boots.
Cold
Working in cold conditions means dressing to keep warm, and your shoes are no exception to this. Insulated work boots are a must if you work outside or are exposed to other cold conditions. Feet not properly insulated against the cold are in danger of frostbite and other cold-related risks.
Moisture
Water-resistant leather boots are a popular choice when working in wet conditions where moisture is an issue. Working outside means being exposed to elements, and almost always puts you at a risk for getting wet. Keeping your feet dry helps protect them against the cold. Water-resistant footwear protects against mold, rot, and fungus growth.
Slippery Surfaces
Slip-resistant shoes are required for a large variety of industries. Healthcare workers, kitchen workers, wait staff, industrial workers, factory workers—the list is almost endless. Slip-resistant shoes come with a sole that reduces the slickness that can cause a fall or accident.
Molten Metals
Working with molten metals presents huge risks. Foundry shoes are made specifically for these types of occupations. These are designed to insulate against the extreme heat of this kind of environment. They prevent hot metals from getting lodged into the shoe’s eyelets. They also frequently come with an easy slip-off design in case of a burn caused by a molten metal splash.
A Few More Things about Work Footwear
Of course, there are a few more factors to consider when buying the right work footwear. You should make sure you feel supported in your arch and ankle, and that you can stand and move in them comfortably. You will also want to be sure they fit well; a loose-fitting shoe can be a work hazard itself. Always make sure the footwear you choose matches the guidelines set by your company, and for the type of work you do. Protect your feet well—they’re all you’ve got to stand on!
Download the photo
Now you can download the Infographic ” Types of Foot Protection” and post it at the workplace and communicate with everyone to be familiar with the types of safety shoes and how to choose the Right footwear that suits the workplace hazard.
Photo of the day: Types of Foot Protection
More photos:
- What are the Best Practices for Managing Subcontractor Risk
- Photo of the day: 10 Essential Safety Tips for Driving in Hot Weather Conditions
- Photo of the day: best workplace safety tips
- Photo of the day: The Importance of Stop Work Authority in Maintaining Workplace Safety
- Photo of the day: Tomorrow’s Reward for Working Safely Today: Cultivating a Culture of Safety
- Photo of the day: Preventing slips and trips at work
- Photo of the day: Learn the DRSABCD action Plan
- Working with Electricity Electrical Accidents Guide for Electrical Workers
- Photo of the day: Hearing Protection Device Selection
- Photo of the day: If An Earthquake Shakes You-Infographic free
- Fire Safety Posters Free Download
- Photo of the day: First Aid for Electrical Burns-Infographic free
- Infographic: First Aid for Cuts and Scrapes free download
- Photo of The day: Work Safe with Lasers-Laser Safety free
- Photo of the day: Working Safely with chemicals and chemical Management
- Photo of the day: Safe work practices when using MEWPs ( updated)
- Photo of the day: Preventing Common Kitchen Hazards
- Photo of the day: Safe handling of Gas Cylinders and lecture bottles
- Photo of the day: Forklift Stability Triangle
- Photo of the day: Defective Tools Safe Work Practice
- Photo of the day: Lift With Your Legs Not With Your Back
- Photo of the day: First Aid for burns
- Photo of the day: The 7 Principles of HACCP
- Photo of the day: Working Safely with Suspended Loads
- Photo of the day: Heat Stroke First Aid and safety posters
- Photo of the day: Near-Miss Reporting and Posters
- Photo of the day: Ergonomic chair and office chair safety tips
- Photo of the day: Whole Body Vibration
- Photo of the day: Substation Safety Equipment
- Photo of the day: Bypassing Safety Controls Rules
- Photo of the day: Lightning Safety Tips
- Photo of the day: Overhead Power lines Clearance
- Photo of the day: Floor Marking
- Photo of the day: Types of Foot Protection
- Photo of the day: Types of Hand Protection
- Photo of the day: Lockout and Tagout Safety
- Photo of the day: Fall Protection Plans
- Photo of the day: Flood Safety Tips
- Photo of the day: Read All Labels Work safe
- Photo of the day: Run Project safely with Crane Hand Signals
- Photo of the day: Flagman and Traffic control
- Photo of the day: Managing Risks of Exposure to Solvents in the workplace
- Photo of the day: Scissor Lift Safety
- Photo of the day: HSE Bulletin Board
- Photo of the day: Arc-Fault Circuit Interrupters (AFCI)
- Photo of the day: Safe use of ladders and step ladders
- Photo of the day: Concrete Truck Driver Hand Signals
- Photo of the day: Extension Cord Safety Tips
- Photo of the day: Protect your Head
- Photo of the day: choosing the right Anchorage
- Photo of the day: Work-Related Asthma
- Photo of the day: Top FIVE Heavy Equipment Construction Site Safety Tips
- Photo of the day: sun safety in the workplace
- Photo of the day: Cannabis and Impairment in the Workplace
- Photo of the day: Position for safety and comfort-Safety Tips
- Photo of the day: Generator Safety
- Photo of the day: Controlling COVID-19 in the Workplace-Physical Barriers
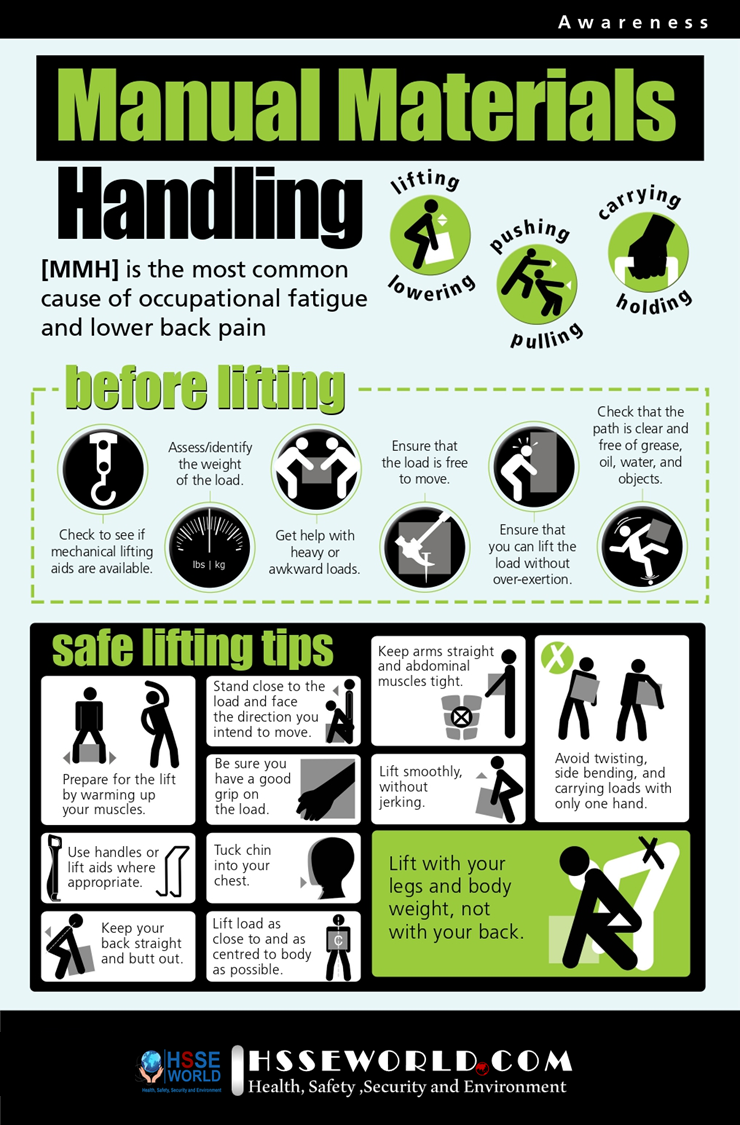
- Photo of the day: Manual Material handling
- Photo of the day: Personal Protective Equipment last resort
- Photo of the day: WHMIS 2015 – Pictograms
- Photo of the day: Indoor Air Quality
- Photo of the day: Noise in the affected workplace
- Photo of the day: Fatigue at Work
- Photo of the day: Don’t be Driven to Distraction
- Photo of the day: working in heat and Humidex Rating
- How to use Plate Clamps Safely: Safety Moment#34
- Photo of the day: Sitting at work
- Photo of the day: 5 ways to reduce the risk of Slipping and Tripping
- Photo of the day: Preventing the spread of contagious illness
- Photo of the day: Incident Investigations
- Photo of the day: 10 Scaffold Safety Essentials
- Photo of the day: Effective Health and Safety Committees
- Photo of the day: New worker Orientation & Safety Orientation checklist
- Photo of the day: Workplace Inspection
- Photo of the day: musculoskeletal disorders
- Photo of the day: Emergency preparedness in the workplace
- Photo of the day: Mental health in the workplace
- Photo of the day: Trenching Safety Tips That Can Save a Life
- Photo of the day: Dangerous Goods Classes
- Photo of the day: Safety Equipment for Confined Spaces
- Photo of the day: Tips to reduce Heat stress in the workplace
- Photo of the day: hierarchy of controls
- Your steps to chemical safety
- H2S Gas and how to handle its Emergency
- Photo of the day: Importance of Mock drill and Fire Action Emergency Procedure
- Photo of the day: Choosing the Right Face Mask and the difference between a respirator and face mask
- Photo of the day: Confined space safety Precautions
- Breath Safely: The Proper Use of Respiratory Protection
- Photo of the day: Electric shock survival
- Photo of the day: Chemical Spill Emergency Response
- Photo of the day: Construction Site fire Safety
- Photo of the day: Confined Space rescue
- Photo of the day: Conveyors Safety Tips