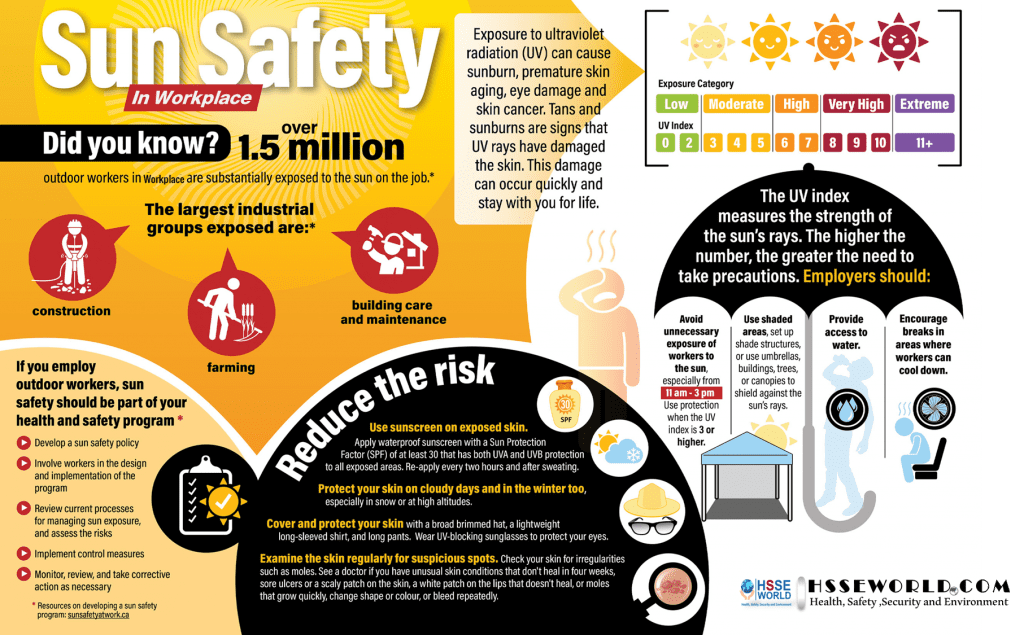
People who work outdoors are vulnerable to the sun’s rays. Exposure to ultraviolet radiation (UV) can cause sunburn, premature skin ageing, eye damage, and skin cancer. Skin cancer is the most common cancer in many workplaces and the rate continues to rise, yet it is one of the most preventable. The photo of today and the infographic outline ways, employers can support outdoor workers, including the development of a sun safety policy, and tips to reduce the risk when working outside.
WHAT IS SUN SAFETY?
If you or your employees work outdoors, you are exposed to the sun. The sun is a workplace hazard that causes the following:
- Health conditions of the skin and eye from over-exposure to solar ultraviolet (UV) radiation, including skin cancer, sunburn, and cataracts, among others.
- Heat stress caused by exposure to the sun
Sun safety is what workplaces do to manage sun exposure.
HOW DANGEROUS IS THE SUN FOR OUTDOOR WORKERS?
For outdoor workers, sun exposure is the primary source of skin cancer and heat stress. Outdoor workers are at a higher risk of both conditions. They often have more sun exposure than the workplace exposure limits.
Between 1.5 million and 5.4 million workers are exposed to the sun on the job. Of these workers, about 67% spend two or more working hours in the sun every workday.
Outdoor workers have up to 3.5 times greater risk of developing skin cancer than indoor workers. Eye damage from long-term exposure to the sun is also a concern, and heat stress is another major issue for outdoor workers.
The good news is that skin cancer, eye damage from the sun, and heat stress are preventable.
HOW CAN WORKPLACES AND WORKERS BE MORE SUN-SAFE?
Workers and workplaces both have a role in workplace sun safety. Workplaces can be more sun-safe by implementing a sun safety program. Workers can follow six simple steps to protect themselves from both solar UV radiation and heat from the sun.
Tips for Employers
The Federal and State Occupational Health and Safety Acts require all employers to put certain strategies in place to minimize sun exposure in the workplace. As a penalty, employers may provide workers’ compensation to workers who get skin cancer as a result of excessive sun exposure at work.
Read the sun-uv-radiation-exposure
Employers can use these sun-safety strategies:
1. Redesign the Workplace.
This involves remodeling the workplace structure and work schedule to limit sun exposure. Ways to achieve these include
- Increase the amount of shade available, using cooling stations, shelters, or tents.
- Cover bright surfaces that reflect ultraviolet light.
- Encourage workers to move their tasks to shaded areas if possible.
- Rotate workers’ shifts to work at different times of the day or rotate between indoor and outdoor tasks, instead of performing outdoor tasks all day, every day.
- Create shaded outdoor areas for breaks in between outdoor tasks.
- Schedule tasks such as mowing to times when the sun’s UV radiation is minimal (such as early in the morning and late in the afternoon).
- Schedule indoor tasks for the times of the day when solar UV radiation is strongest, such as noon.
2. Create Sun Safety Policies and Training
One way of passing the message across to employers is to create a culture around it. Employers can incorporate sun safety information into workplace wellness programs. One way of doing this is organizing programs and seminars to teach employees about sun safety and the risks of exposure to ultraviolet light.
Information about sun safety may also be sent via e-mails, included in regular newsletters, or pasted on office notice boards. This keeps workers constantly aware of the risks of overexposure to the sun and what they need to do to minimize it.
3. Provide Personal Sun Protection
All outdoor workers should be provided with the appropriate personal protective equipment and ensure it is used appropriately
These include protective work clothing consisting of a long-sleeved shirt and long pants; hats that cover most parts of the head including the face, ears, and neck; sunglasses, and; broad-spectrum, SPF30+ water-resistant sunscreen.
Tips for Employees
To reduce sun exposure at work, employees can follow these simple rules:
1. Minimize exposure to sunlight at peak hours (between 10 am and 3 pm)
2. Wear protective clothing (clothing, a hat, and sunglasses). Clothing should have the following features that protect from UV radiation.
Implement sunglasses-safety-and-eye-health
- Dark-colored fabrics such as reds, blues, and greens prevent penetration of UV radiation.
- Close weave fabrics.
- Long-sleeve shirts, a collar, and long pants.
- Fabrics with high ultraviolet protective factor (UPF) values.
- Hat with a broad base to shade both the face and the back of the neck.
- Glasses with a high eye protection factor (EPF). Sunglasses with EPF ratings of 9 and 10 (out of 10) are preferred.
3. Use Sunscreens
Sunscreens protect the skin from UV radiation, preventing skin cancer and early skin aging. You should choose sunscreens that are water-resistant, broad-spectrum (blocks both UVA and UVB), and have sun protective factor (SPF) of at least 30. Anything below these will compromise your skin’s protection.
How to Apply Sunscreens
- Apply thoroughly over clean, dry skin for at least 15 minutes before going outdoors. This is because it takes this long for the skin to completely absorb the sunscreen. Applying sunscreen while in the sun will not protect the skin from solar UV radiation.
- Apply sunscreen to all exposed skin, including your neck, face, ears, and all exposed parts of your feet and legs. Ask someone to help you apply it to areas that are hard to reach such as your back.
- If you have thinning hair, apply sunscreen to your scalp. You can also apply a lip balm that contains sunscreen with SPF 15+ to protect your lips.
- Reapply sunscreen after every two hours outdoors and immediately after swimming. Failing to reapply sunscreens defeats its purpose. Some people can get sunburned because of this.
- Remember to apply sunscreen every time you go outside. The risk of being exposed to UV radiation is always present during the day, even on cloudy days.
Sun safety should be a priority in all workplaces. The consequences of overexposure are too great to ignore. These sun-safety strategies need to be emphasized continuously. Doing this will not only maintain employee health but will also reduce organizational costs and help employers to retain their best talents.
Taming the Itch: Powerful Psoriasis Self-Care Tips for Soothed Skin and a Calmer You
Download Infographic
Sun safety in the workplace
More Photos
- What are the Best Practices for Managing Subcontractor Risk
- Photo of the day: 10 Essential Safety Tips for Driving in Hot Weather Conditions
- Photo of the day: best workplace safety tips
- Photo of the day: The Importance of Stop Work Authority in Maintaining Workplace Safety
- Photo of the day: Tomorrow’s Reward for Working Safely Today: Cultivating a Culture of Safety
- Photo of the day: Preventing slips and trips at work
- Photo of the day: Learn the DRSABCD action Plan
- Working with Electricity Electrical Accidents Guide for Electrical Workers
- Photo of the day: Hearing Protection Device Selection
- Photo of the day: If An Earthquake Shakes You-Infographic free
- Fire Safety Posters Free Download
- Photo of the day: First Aid for Electrical Burns-Infographic free
- Infographic: First Aid for Cuts and Scrapes free download
- Photo of The day: Work Safe with Lasers-Laser Safety free
- Photo of the day: Working Safely with chemicals and chemical Management
- Photo of the day: Safe work practices when using MEWPs ( updated)
- Photo of the day: Preventing Common Kitchen Hazards
- Photo of the day: Safe handling of Gas Cylinders and lecture bottles
- Photo of the day: Forklift Stability Triangle
- Photo of the day: Defective Tools Safe Work Practice
- Photo of the day: Lift With Your Legs Not With Your Back
- Photo of the day: First Aid for burns
- Photo of the day: The 7 Principles of HACCP
- Photo of the day: Working Safely with Suspended Loads
- Photo of the day: Heat Stroke First Aid and safety posters
- Photo of the day: Near-Miss Reporting and Posters
- Photo of the day: Ergonomic chair and office chair safety tips
- Photo of the day: Whole Body Vibration
- Photo of the day: Substation Safety Equipment
- Photo of the day: Bypassing Safety Controls Rules
- Photo of the day: Lightning Safety Tips
- Photo of the day: Overhead Power lines Clearance
- Photo of the day: Floor Marking
- Photo of the day: Types of Foot Protection
- Photo of the day: Types of Hand Protection
- Photo of the day: Lockout and Tagout Safety
- Photo of the day: Fall Protection Plans
- Photo of the day: Flood Safety Tips
- Photo of the day: Read All Labels Work safe
- Photo of the day: Run Project safely with Crane Hand Signals
- Photo of the day: Flagman and Traffic control
- Photo of the day: Managing Risks of Exposure to Solvents in the workplace
- Photo of the day: Scissor Lift Safety
- Photo of the day: HSE Bulletin Board
- Photo of the day: Arc-Fault Circuit Interrupters (AFCI)
- Photo of the day: Safe use of ladders and step ladders
- Photo of the day: Concrete Truck Driver Hand Signals
- Photo of the day: Extension Cord Safety Tips
- Photo of the day: Protect your Head
- Photo of the day: choosing the right Anchorage
- Photo of the day: Work-Related Asthma
- Photo of the day: Top FIVE Heavy Equipment Construction Site Safety Tips
- Photo of the day: sun safety in the workplace
- Photo of the day: Cannabis and Impairment in the Workplace
- Photo of the day: Position for safety and comfort-Safety Tips
- Photo of the day: Generator Safety
- Photo of the day: Controlling COVID-19 in the Workplace-Physical Barriers
- Photo of the day: Manual Material handling
- Photo of the day: Personal Protective Equipment last resort
- Photo of the day: WHMIS 2015 – Pictograms
- Photo of the day: Indoor Air Quality
- Photo of the day: Noise in the affected workplace
- Photo of the day: Fatigue at Work
- Photo of the day: Don’t be Driven to Distraction
- Photo of the day: working in heat and Humidex Rating
- How to use Plate Clamps Safely: Safety Moment#34
- Photo of the day: Sitting at work
- Photo of the day: 5 ways to reduce the risk of Slipping and Tripping
- Photo of the day: Preventing the spread of contagious illness
- Photo of the day: Incident Investigations
- Photo of the day: 10 Scaffold Safety Essentials
- Photo of the day: Effective Health and Safety Committees
- Photo of the day: New worker Orientation & Safety Orientation checklist
- Photo of the day: Workplace Inspection
- Photo of the day: musculoskeletal disorders
- Photo of the day: Emergency preparedness in the workplace
- Photo of the day: Mental health in the workplace
- Photo of the day: Trenching Safety Tips That Can Save a Life
- Photo of the day: Dangerous Goods Classes
- Photo of the day: Safety Equipment for Confined Spaces
- Photo of the day: Tips to reduce Heat stress in the workplace
- Photo of the day: hierarchy of controls
- Your steps to chemical safety
- H2S Gas and how to handle its Emergency
- Photo of the day: Importance of Mock drill and Fire Action Emergency Procedure
- Photo of the day: Choosing the Right Face Mask and the difference between a respirator and face mask
- Photo of the day: Confined space safety Precautions
- Breath Safely: The Proper Use of Respiratory Protection
- Photo of the day: Electric shock survival
- Photo of the day: Chemical Spill Emergency Response
- Photo of the day: Construction Site fire Safety




