The storage and use of flammable and combustible liquids pose significant risks in the workplace. To mitigate these risks and ensure compliance with safety regulations, it is crucial for employers and employees to adhere to the guidelines set forth by the Occupational Safety and Health Act. To assist in this endeavor, we have compiled a comprehensive Flammable and Combustible Storage Checklist. This checklist serves as a valuable resource for evaluating and enhancing safety measures in the storage and handling of these hazardous substances. While it is important to note that this checklist is not exhaustive and cannot guarantee full compliance with all regulations, it provides a solid foundation for identifying potential safety concerns and prompts necessary corrective actions.
Flammable Liquid Storage Safety Moment

The Checklist
This checklist has been compiled to help employers and employees comply with the requirements of the Occupational Safety and Health Act, (Reference 29 CFR 1910 and 1926 of the Federal OSHA Standards) regarding the storage and use of flammable and combustible liquids. This checklist is only a guide. The use of it does not necessarily assure full compliance with all state and federal regulations. This checklist is designed in such a manner that a negative answer indicates a need for safety attention.
Tanks (IN General)
- Are tanks made of steel (unless they fit the exception as noted)?
- If the tank is of inlined concrete, is it being used to store a flammable or combustible liquid having a gravity of 40 API or heavier?
- Is the spacing between any two tanks housing flammable or combustible liquids, not less than three feet?
Also Read: Navigate Flammable and Combustible Liquid Safety
- Is the separation between an LP gas container and a flammable or combustible liquid storage tank at least twenty feet?
- Does every above-ground storage tank have a pressure-relieving system?
- If tanks storing Class I liquids are located adjacent to buildings, are the vents arranged to be released at a safe point outside the building?
- Is the area around the tank(s) provided with drainage or diked as provided?
- Are tank supports on a firm foundation? Are these supports made of concrete, masonry, or protected steel?
- If the tank(s) is inside the building, does it meet the requirements of OSHA?
- If manual gaging is independent of the fill pipe, does it have a liquid-tight cap or cover?
Outside Above Ground Storage
- Is the area free of weeds, debris, and other combustible materials not necessary for storage?
- If the quantity exceeds 1,100 gallons, is there a minimum distance of ten feet between the building and the nearest container?
- Is the storage area either graded to divert possible spills away from buildings or surrounded by a curb at least six inches high?
- If curbs are used are there provisions for draining accumulations of ground or rainwater of spills of flammable or combustible liquids?
- Do the drains terminate at a safe location?
- Are suitable fire control devices available?
- Is the distance between any two of the storage tanks at least three feet?
- If storage tanks are placed in an irregular fashion, are the inside tanks available for firefighting purposes?
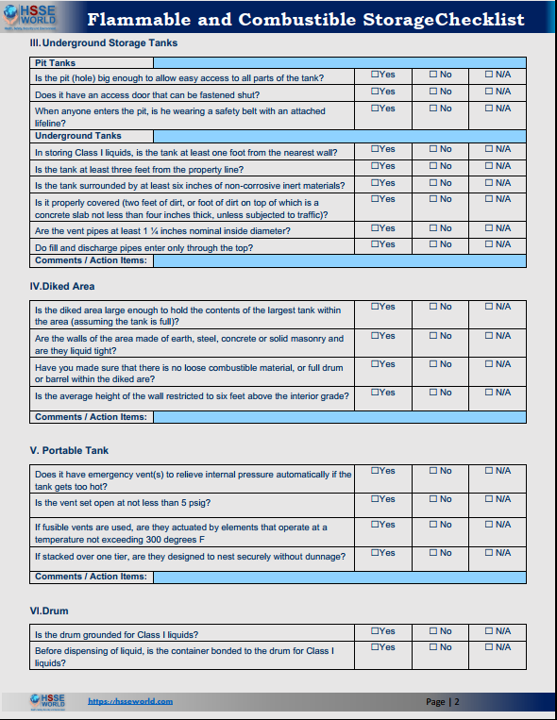
Underground Storage Tanks
Pit Tanks
- Is the pit (hole) big enough to allow easy access to all parts of the tank?
- Does it have an access door that can be fastened shut?
- When anyone enters the pit, is he wearing a safety belt with an attached lifeline?
Underground Tanks
- In storing Class I liquids, is the tank at least one foot from the nearest wall?
- Is the tank at least three feet from the property line?
- Is the tank surrounded by at least six inches of non-corrosive inert materials?
- Is it properly covered (two feet of dirt, or a foot of dirt on top of which is a concrete slab not less than four inches thick, unless subjected to traffic)?
- Are the vent pipes at least 1 ¼ inches nominal inside diameter?
- Do fill and discharge pipes enter only through the top?
Diked Area
- Is the diked area large enough to hold the contents of the largest tank within the area (assuming the tank is full)?
- Are the walls of the area made of earth, steel, concrete, or solid masonry and are they liquid-tight?
- Have you made sure that there is no loose combustible material or full drum or barrel within the dike area?
- Is the average height of the wall restricted to six feet above the interior grade?
Portable Tank
- Does it have an emergency vent(s) to relieve internal pressure automatically if the tank gets too hot?
- Is the vent set open at not less than 5 psig?
- If fusible vents are used, are they actuated by elements that operate at a temperature not exceeding 300 degrees F
- If stacked over one tier, are they designed to nest securely without dunnage?
Drum
- Is the drum grounded for Class I liquids?
- Before dispensing of liquid, is the container bonded to the drum for Class I liquids?
- Is the drum on metal supports if inside? (Recommended)
Safety Can
- Does it have a spring-closed lid and spout cover?
- Is it designed to prevent spills and to relieve internal pressure of expanding vapors?
- Does it have a maximum safe capacity of five gallons (except for Class IA and this has a safe capacity of two gallons)?
- If stacked over one tier, are they designed to nest securely without dunnage?
- Does it have a flame arrester?
Storage Cabinet
Capacity
- Is it ascertained that not more than 60 gallons of Class I and Class II liquids or not more than 120 gallons of Class III liquids are stored in any storage cabinet?
Metal Cabinets
- Is it labeled “Flammable –Keep Fire Away”?
- Is it made of at least number 18 gauge sheet iron?
- Is it double-walled with 1 ½ inches air space?
- Is the door provided with a 3-point lock?
- Is the door raised at least 2 inches above the bottom of the cabinet?
Wooden Cabinets
- Is it made of an approved grade of plywood that is at least 1 inch in thickness?
- Are all joints rabbetted and fastened in two directions with flathead wood screws?
- If more than one door is used, is there a rabbetted overlap of not less than 1 inch?
Inside Storage Room
- Are all openings provided with approved self-closing fire doors?
- Is the room provided with either a gravity or mechanical exhaust ventilation system?
- Is the ventilation system designed for a complete change of air within the room at least six times per hour?
- If a mechanical exhaust system is being used, is the control switch outside the door, and is it connected to the light fixture system?
- Does the room have one clear aisle that is at least three feet wide?
- If containers are over thirty (30) gallons in capacity, did you remember not to stack one upon the other?
- Are things stacked in the storage room so as not to limit the use of exits or areas normally used for safe egress?
- Is the room liquid-tight where walls join the floors?
- Does the room have either: (1) raised sills at least four inches high; (2) a floor at least four inches below the surrounding floor; or (3) an open-grated trench inside the room that drains to a safe location?
- Does the total allowable quantity stored within the room comply with the room comply with Table H-13?
- Are all storage room areas posted “No Smoking”?
- If wood is used for shelving, dunnage or racks, is it at least one inch in thickness?
- Is there a fire extinguisher (12B minimum) located within ten feet of the door?
- If the storage building is located fifty feet or less from a building or line of adjoining property that may be built upon, does the exposing wall have a fire resistance rating of at least two hours?
- If containers are stacker in piles, are they separated by pallets or dunnage where necessary to assure stability?
Storage Inside Building
- Are containers stored so as not to limit the use of stairways, exits or other means of egress?
- Are the containers being used the approved type?
- In office areas, is there only enough of these liquids for maintenance and operation?
- Is storage being done in accordance with Table H-14 or Table H-15?
Inside Tanks
- If inside tanks are being used, do they meet the requirements as listed?
- Do the vents discharge vapors outside the building?
- Are the employing and filling connections that are made and broken located outside and free from any source of ignition?
- Does it have an automatic-closing heat-activated valve on each withdrawal connection to prevent continued flow in the event of fire in the vicinity?
- Is it provided with a means to prevent overflow into the building?
Storage in a Public Warehouse
- Is storage done in accordance with Table H-14 or Table H-15?
Storage in a Warehouse or Storage Building
- Is storage in accordance with Table H-14 or Table H-15?
- If the building is located 50 feet or less from another building, does the exposed wall have a fire-resistance rating of at least 2 hours?
Incidental Storage
- Are the liquids stored in tanks or closed containers?
- Is the amount of Class IA liquid stored not in excess of 25 gallons?
- Is the amount of Class IB, IC, II, or III liquids stored not in excess of 660 gallons (in a single portable tanks)?
Storage In Flood Areas
Vertical Tanks
- Is the amount of liquid to be stored considered safe for the tank during a flood (unless it has a guiding structure)?
- If the tank is located on an exposed point or on the bank of a shore line, is the structure able to withstand a unit force up to 50 pounds per square foot?
- Are the structural guides designed to give free rise to the tank and are they made of non-combustible materials?
- If there is no public water supply, is water available to fill any/all tanks that are practically empty?
- If the tank is horizontal and more than 70% of the tank would be submerged during a flood, is it attached to a foundation of concrete or of steel and concrete?
Fire Protection or Control
- Are an adequate number of portable fire extinguishers and control equipment provided for the special hazards that exist?
- Is the water supply adequate both in volume and in pressure to supply all equipment needed?
- Are all fire protection facilities maintained and periodically checked and tested?
Tank Cars
- Are the tanks cars separated from warehouses, plant buildings or adjoining property lines by a distance of 25 feet for Class I and by 15 feet for Class II and III liquids?
- Are the valves self-closing, and are they held open manually except when automatic means are provided for shutting off the flow?
- Are bonding facilities provided?
Dispensing Station
- Are the dispensing units either mounted on a concrete island or protected against collision damage?
- Does the area have an approved mechanical or gravity ventilation system?
- Is there an easily accessible switch (es) or a circuit breaker (s) at a location remote from the dispensing devices?
- Is there a “No Smoking” sign(s)?
- Is there an appropriate fire extinguisher?
Industrial Plants
- Are the processing buildings made of fire-resistant, non-combustible or heavy timber construction?
- If the processing building is enclosed, is it ventilated at a rate of at least 1 cubic foot per minute per square foot of solid floor area?
- Is emergency drainage provided to direct these liquids to a safe location?
- If Class I liquids are being used, is the area provided with explosion venting?
- Is proper fire control available?
- Does the plant have an approved automatic sprinkler system?
Construction
- Are the combustible materials piled no higher than twenty feet?
- Are the driveways between and around combustible storage piles at least fifteen feet wide?
- Is there at least ten feet between outside stored combustibles and any building or structure?
- Are the portable tanks at least twenty feet from any building?
- Is there at least one portable fire extinguisher with a rating of not less than 20-B units at any outside storage area?
- Is this extinguisher not less than 25 feet and not more than 75 feet from the area?
Tables
Table H-12 Maximum Allowable Size of Containers and Portable Tanks
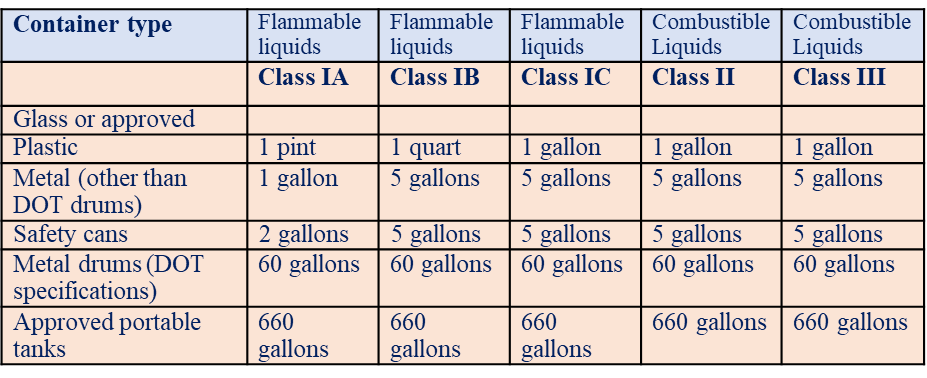
Table H-13 Storage In Inside Rooms

Table H-14 Indoor Container Storage

Checklist Snapshot

Conclusion:
The Flammable and Combustible Storage Checklist provided serves as a valuable tool for employers and employees to assess and enhance safety protocols in the storage and handling of flammable and combustible liquids. By diligently addressing the checklist items and taking necessary corrective actions, workplaces can minimize the risk of accidents, injuries, and property damage associated with these hazardous substances.
It is important to remember that this checklist is not exhaustive and should be supplemented with regular safety training, professional guidance, and compliance with all relevant state and federal regulations. Together, we can create a safer working environment by prioritizing the proper storage and use of flammable and combustible liquids.
Download
To download a free copy of the Flammable and Combustible Storage Checklist, please click the button below.
Flammable and Combustible Storage Checklist
PDF COPY
WORD COPY
More Forms
- Navigating the Risks: The Ultimate Guide to Safety When Working Near Water
- Downloadable Kitchen Safety Inspection Checklist for Restaurants
- Mastering LOTO: Protecting Workers with Energy Isolation and Isolation Confirmation Certificates
- Flammable and Combustible Storage Checklist Free Download
- Secure Your Lifts:Guidelines for Safe Lifting Operations Free Planning Tool
- Sample of Accident Prevention Program ( APP) Template for General Industry Free Download
- Free ISO 14001:2015 Environmental Management System Audit Checklist Download
- Guides for Walking and Working Surfaces Safety Program
- Workshop Safety Guideline and free Posters
- Free Ergonomics Checklist for General Industry
- Work Area Safety Checklist
- Machine Safety and 43-Equipment Inspection Checklists
- Scaffold Safety self Audit and checklist
- Hot Work Controls and its Permit to work Form
- Safety Observation Report Template
- Forklift Operator’s Daily Checklist and safety Tips
- Inspecting Fall Protection Equipment Forms
- Templates: HSE Incentives and rewards
- 35 Inspection forms for Rig Check
- Chemical Risk Assessment form
- 22-Safety Inspection Checklists
- Safety Task Assessment Form
- Suspended Scaffold Pre-Operation Inspection Checklist
- Photo of the day: New worker Orientation & Safety Orientation checklist
- Grating-Decking-Floor- handrail-Removal Form
- Electrical Inspection Checklists
- E-Books: Fire Safety Logbook templates
- General Safety Guidelines and Employee Acknowledgment form
- Annual Internal Audit Form
- Mobile Scaffold Inspection checklist
- Simultaneous Operation (SIMOPS) checklist
- Temporary Construction Facilities (TCF) Inspection checklist
- HIRA, HSE Hazards & Effects Management Process (HEMP) & Risk Register Template
- Hazard Identification Plan (HIP) Template
- Ladder Inspection Form
- Free Pre-Startup Safety Review Checklist (PSSR)
- Hazard Identification Checklist
- Workplace Housekeeping Checklist
- ISO 45001:2018 READINESS CHECKLIST
- Lifting Plan Audit Checklist
- Job Safety Analysis (JSA) Forms What’s Right and Wrong?
- Electrical Isolation Permit to Work forms and checklist
- Canteen Inspection Checklist
- Work at Height Checklist
- Health Safety at Work Improvement Action Plan
- Fire Pump Daily Inspection Checklist
- Construction Site Traffic Management Plan (CSTMP) Guidance
- Safety Templates: COVID-19 Safety Plan
- Workplace Safety Inspections Forms
- Lock Removal Form
- Templates: Management of Change NEW Modified Equipment Safety Checklist
- Lifeline & Harness Inspection Guide checklist
- Contractor Pre-qualification Questionnaire Checklist
- Fall safety at construction checklist
- Construction safety Inspection checklist
- Equipment Safe Operating Procedures- SOP 61 checklist
- Permit to Work (PTW ) AUDIT CHECKLIST
have more safety resources at safetybagresources