Organizations desire to continuously upgrade their health and safety improvement. Improvement in health and safety at work performance needs a planned, disciplined, and managed approach. This is promoted from an effective and structured health and safety improvement plan. The creation and application of a safety improvement plan help cooperatives formalize its planned safety improvement efforts to address and monitor progress on key focused areas as part of an ongoing improvement cycle to achieve higher levels of safety performance.
An Effective Safety Improvement Plan Offers Opportunities to Achieve Several Important Outcomes:
- Establish incremental improvement milestones through targeted safety improvement goals for achievement between the full assessment cycles.
- Involve the leadership to concentrate on the critical barriers and priorities hindering safety performance.
- Demonstrate leadership accountabilities and commitment to achieve planned safety improvement.
- Provide the means to monitor and review progress on safety improvement efforts.
- Provides a mechanism to enhance employee involvement in health and safety improvement activities.
- Fosters employee communication by providing a common direction and commitment to achieving safety goals and improvement initiatives.
Preparing for the Plan
Consider how the annual plan will be prepared, who will be involved in the plan development, when will the planning process occur, and the sources for understanding the context for the possible safety improvement areas. Leadership engagement is essential to the plan development and execution of the plan. The top management should champion the planning effort, setting expectations for an actionable and attainable plan that addresses the important areas for safety improvement. An effective approach is to develop the safety improvement plan through a collaborative process involving representatives from the leadership staff, key front-line leaders, and safety coordinator. A plan developed in isolation minimizes understanding and buy-in for successful implementation. Identify who will lead the planning process. Make a Selection of an individual with the organizational competencies to guide the process and involve others for critical input. As needed, seek assistance from the statewide safety professional. The Health and Safety Professional can serve as a Beneficial Resource in several Areas Including:
Provision of a source of aspiration evaluation for highlighting development areas, identifying available resources to support targeted improvements, providing input on applicable best safety practices, and facilitating the plan development.
Furthermore, the planning approach, consideration should be given to sources for understanding and identifying possible areas for Health and safety improvement. For example, the following outlines four possible sources to consider.
Enhance Leadership and Culture:
Leadership and safety culture has an enlightening effect on safety outcomes. Understand the current state with regards to leadership engagement, organization culture, and its effect on safety. Assess the strengths and weaknesses and understand areas to build on the strengths and close the gaps in areas of weaknesses within leadership and culture.
Address Key Attention Areas from Assessment Process Results:
Having an understanding of the outcome both from the formal three-year assessment and self-assessments. This covers understanding health and safety performance results and how the cooperative compare with benchmark results. Acknowledge the identified attention areas and how to address them within the safety improvement plan.
Strengthen Safety Practices
Recognize opportunities to strengthen safety practices by achieving incremental movement to best practices. This begins by understanding the elements of an effective safety system, model safety programs, and applied safety best practices from other cooperatives and industries. Avoid the trap of accepting the status quo. Safety process strengths should be leveraged and refined for further improvement.
Increase Knowledge and Awareness
Recognize training opportunities to increase knowledge and awareness of safety. Training can cover several areas including:
- Compliance, procedures, and processes.
- Safety improvement concepts.
- Safety program tools and methods.
- Leadership best practices, to name a few.
Consider critical knowledge gaps and consider opportunities to address them within the health and safety improvement plan.
Key Steps for Developing a Safety Improvement Plan
The following suggested steps in developing a safety improvement plan are:
1. Recognize Opportunities for Improvement.
This begins by considering the above sources and gaining a candid view of the current state of safety practices and performance. List and understand the possible areas for improving safety improvement. Identify high levels of goals for safety improvement. Consider establishing high-level safety goals to achieve within the three-year safety assessment cycle. What improvements do we want to achieve in the next three years? State goals in a clear context so that it is understood what is to be achieved. Keep in mind a continuous improvement effort and identify 2-4 four meaningful goals that can be realistically attained. Annually review these goals and update them as warranted. Avoid overemphasis on injury rates, try to focus on activity-based goals that have been proven to reduce injury rates if effectively achieved.
2. Identify and Prioritize Safety Improvement Initiatives.
Outline the most important initiatives or actions to achieve high-level goals. Focus efforts on a few critical initiatives taking care not to overwhelm the plan with too many actions that may be difficult to be supported within the organization’s current resource capacity. It is important to state these initiatives into actionable terms so that it is clear what is to be done and assignments can be made to individuals or teams who have the capacity, competencies, and resources to take action.
3. Organize a Plan for Action.
Formulate the goals and initiatives into an organized plan with clear assignments, the timeline for achievement, and identified budget and resources. Define a process to monitor progress. Decide on an approach to regularly review progress on the safety improvement plan. This can be done at the leadership staff, through the formal safety committee, or by the planning team who developed the plan. The cooperative build organization discipline to keep the safety improvement plan relevant and that meaningful progress must be made towards implementation.
4. Communicate the Safety Improvement Plan.
The final step is to communicate the plan to employees. The communication provides an opportunity to engage the employees on the organization’s expectations, commitment, and efforts to improve safety.
5. Define a Process to Monitor Progress.
Decide on an approach to regularly review progress on the safety improvement plan. This can be done at the leadership staff, through the formal safety committee, or by the planning team who developed the plan. The cooperative build organization discipline to keep the safety improvement plan relevant and that meaningful progress must be made towards implementation.
6. Communicate the Safety Improvement Plan.
The final step is to communicate the plan to employees. The communication provides an opportunity to engage the employees on the organization’s expectations, commitment, and efforts to improve safety.
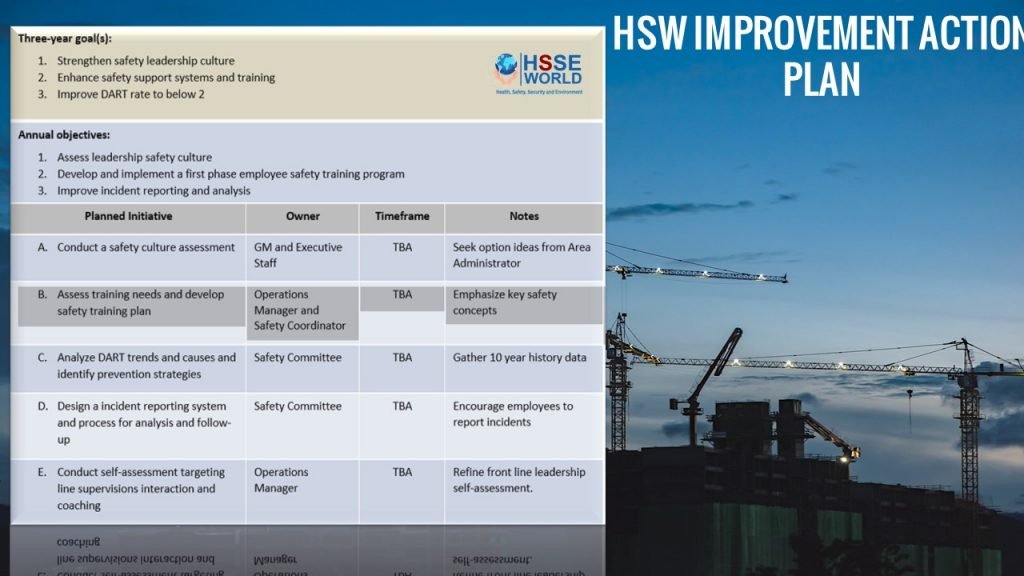
Example of Action Plan
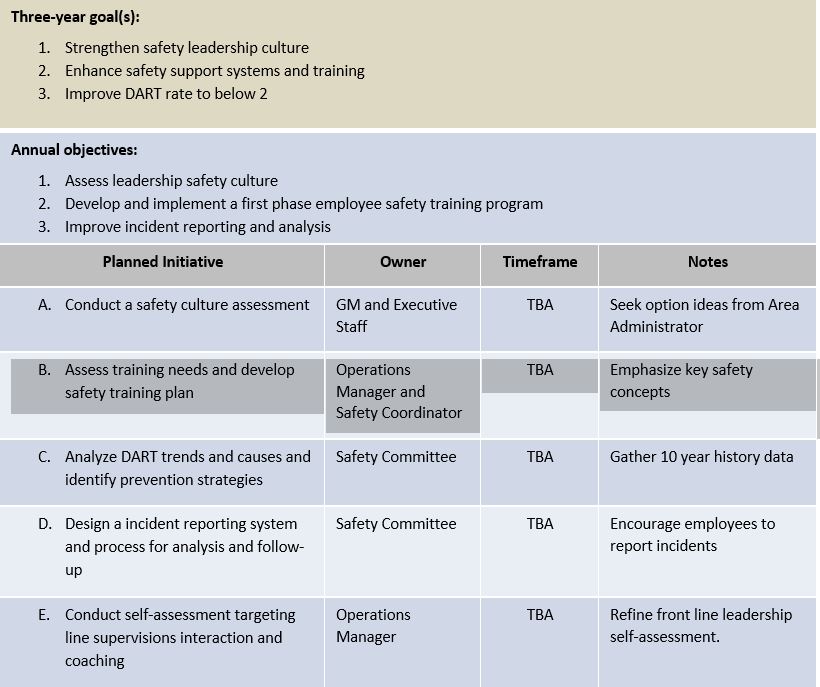
Download the Form
More Forms
- Camp Inspection form
- Machines Access Control Inspection Checklists
- Lift Plan Form
- Slips,Trips and Falls checklist
- Emergency Drill Table Top meeting Form
- Emergency Drill After Action Review form
- Compressed Gas Cylinders Access Control Inspection Checklist
- Competent Person Designation form
- Contractor Weekly HSE Report Form
- Safety Inspection Form
- Incident Report Form
- Job Hazard Analysis form
- OSHA Inspection Checklist 8-Pages
- Process Safety Management (PSM) Compliance checklist
- Portable Ladder Self Inspection checklist
- Scaffold Register and Inspection Checklist
- CRANE INSPECTION REPORT
- Laboratory Inspection Checklist Form
- Electric Arc Welding and Cutting Checklist
- Crane Suspended Personnel Platform (MANBASKET) Permit
- Pressure Testing Checklist
- Hygiene and Sanitation Inspection Checklist
- Permit to Work (PTW ) AUDIT CHECKLIST
- Equipment Safe Operating Procedures- SOP 61 checklist
- Construction safety Inspection checklist
- Fall safety at construction checklist
- Contractor Pre-qualification Questionnaire Checklist
- Lifeline & Harness Inspection Guide checklist
- Templates: Management of Change NEW Modified Equipment Safety Checklist
- Lock Removal Form
- Workplace Safety Inspections Forms
- Safety Templates: COVID-19 Safety Plan
- Construction Site Traffic Management Plan (CSTMP) Guidance
- Fire Pump Daily Inspection Checklist
- Health Safety at Work Improvement Action Plan
- Work at Height Checklist
- Canteen Inspection Checklist
- Electrical Isolation Permit to Work forms and checklist
- Job Safety Analysis (JSA) Forms What’s Right and Wrong?
- Lifting Plan Audit Checklist
- ISO 45001:2018 READINESS CHECKLIST
- Workplace Housekeeping Checklist
- Hazard Identification Checklist
- Free Pre-Startup Safety Review Checklist (PSSR)
- Ladder Inspection Form
- Hazard Identification Plan (HIP) Template
- HIRA, HSE Hazards & Effects Management Process (HEMP) & Risk Register Template
- Temporary Construction Facilities (TCF) Inspection checklist
- Simultaneous Operation (SIMOPS) checklist
- Mobile Scaffold Inspection checklist
- Annual Internal Audit Form
- General Safety Guidelines and Employee Acknowledgment form
- E-Books: Fire Safety Logbook templates
- Electrical Inspection Checklists
- Grating-Decking-Floor- handrail-Removal Form
- Photo of the day: New worker Orientation & Safety Orientation checklist
- Suspended Scaffold Pre-Operation Inspection Checklist




