The GATE HAZOP Method
This book describes the GATE HAZOP Method, the Stream-Based HAZOP. The GATE Method addresses all the problems listed below. Significant features of the method include:
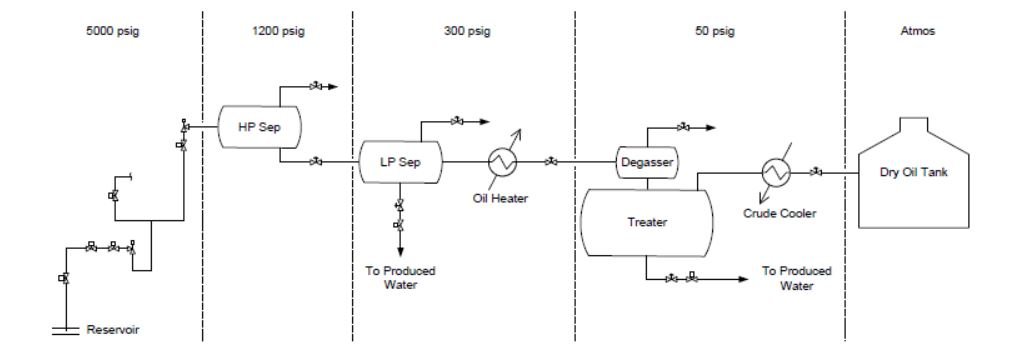
- Stream-based nodes for the FLOW discussions. A stream-based node follows an identifiable stream from its inception to a logical termination point. The graphic below is a single stream-based node for a produced oil stream from the reservoir to the Dry Oil Tank.
- Two-part process: The stream-based nodes are ideal for the FLOW discussion, but equipment-based nodes (typical HAZOP nodes) are necessary for the PRESSURE, TEMPERATURE, and LEVEL safeguarding discussions.
- Use of LOPA rules to simplify and improve risk assessment.

HAZOP – A Critically Important Process
Everyone remembers their first HAZOP. Mine was in 1991. It was the HAZOP of one of my designs. I was intrigued. I was humbled by the results. The HAZOP is probably the most commonly used method for process hazard analysis (PHA). Needless to say, it’s important to get it right. Yet every HAZOP I’ve attended and facilitated over the last 25 years has left something to be desired. After each, I’ve pondered how it could be done more effectively.
This book is the result of 25 years of pondering.

What’s Wrong with HAZOPs?
There are several main reasons why typical HAZOPs are not as effective as they could be including:
- Tunnel vision. Typical HAZOPs focus on one equipment item at a time (equipment-based nodes). The focus on small nodes obscures the big picture. Systems issues might be missed; people not already familiar with the process may not be aware of the interconnections between equipment items and between systems. It is particularly difficult to follow recycle streams and process/process heat transfer.
- HAZOPs are supposed to identify operability issues, but there is no explicit consideration of operability in a typical HAZOP and no effective way to identify operability issues. Success at identifying operability issues depends more on having the right people in the room (experienced operators) than on the process itself.
- Guideword overlap – The guidewords for a typical HAZOP are Flow, Pressure, Temperature, and Level. But flow deviations cause most pressure, temperature, and level deviations. Discussing all four of the guidewords duplicates effort and causes tedium.
- HAZOP reports are difficult to read and therefore are not used for much after the HAZOP.
- Most people don’t enjoy HAZOPs and since they often run for days or weeks at a time, the resulting tedium impacts the effectiveness of the process.
- Risk assessment in HAZOPs is often ambiguous and weak. Ineffective risk assessment generates two problems:
a. Significant hazards might be missed.
b. Can result in a large number of spurious recommendations that occupy the design team’s time, are difficult to close, and contribute little to improving process safety.
Contents
The Contents of HAZOPS Should BE fun
- Preface
- Section I: Discussion of the Method
- Chapter 1: HAZOP Process Overview
- Chapter 2: What’s Wrong with HAZOPs?
- Chapter 3: Stream-based Nodes
- Chapter 4: Two-Part Process
- Chapter 5: Risk Assessment in HAZOPs
- Chapter 6: Summary of the GATE HAZOP Process
- Section II: Integration with Other Studies
- Chapter 7: Procedure HAZOPs
- Chapter 8: Control System Review
- Section III: Cognitive and Psychological Factors
- Chapter 9: Cognitive and Psychological Factors
Download the book
HAZOPS Should BE fun-The Stream-Based HAZOP
More Downloads
- E-Books: Healthcare Hazard Control & Safety Management
- E-Books: Safety, Health and Working Conditions Training Manual
- E-Books: Energy Efficiency in Water and Wastewater Facilities
- E-Books: Fire Service Features of Buildings and Fire Protection Systems
- E-Books: Evaluation of Fire Safety free download
- E-Books: PPE for Chemical, Biological, and Radiological Hazards free
- E-Books: Changing the Workplace Safety Culture free download
- E-Books: Site Emergency Planning Workbook
- E-Books: Load Restraint Guide
- E-Books: Essential Practices for Creating, Strengthening, and Sustaining Process Safety Culture
- E-Books: System Safety Engineering and Risk Assessment
- E-Books: Permit-Required Confined Spaces
- E-Books: Is it Safe to Enter Confined Space?
- E-Books: 5-Minute Workplace Safety Talks
- E-Books: Safety Culture and High-Risk Environments
- E-Books: Practical Guide to Industrial Safety
- E-Books: Slip, Trip, and Fall Prevention for Healthcare Workers
- E-Books: Health and Safety at Work Key Terms
- E-Books: Fundamentals of Process Safety Engineering
- E-Books: Gas Detection Hand Book
- E-Books: Occupational health and safety management systems ANSI-AIHA-z10-2012
- E-Books: Hot Work on Drums and Tanks
- E-Books: Human Fatigue Risk Management
- E-Books: Guidelines for the provision of facilities and general safety in the construction industry
- E-Books: Handbook of Training in Mine Rescue and Recovery Operations ( 2021)
- E-Books: Code of Practice for the Safe Use of Lifting Equipment – Edition 9 (Nov 2019)
- E-Books: Free Forklift Health and Safety Best Practices Guideline
- E-Books: Handbook of Hazardous Chemical Properties
- E-Books: Human Performance Improvement through Human Error Prevention
- E-Books: Principles Of Fire Risk Assessment In Buildings
- E-Books: Investigation of Occupational Accidents and Diseases
- E-Books: Radiation Protection and Safety in Industrial Radiography
- E-Books: Basic Guide to System Safety, Third Edition
- E-Books: Food Safety Management-A Practical Guide for the Food Industry
- E-Books: Safety identification: Escape and evacuation plan signs- ISO 23601
- E-Books: Safety at Work
- E-Books: The Safety-Critical Systems Handbook 4th edition
- E-Books: Fundamental principles of occupational health and safety
- E-Books: Fire Safety Risk assessment Guide – Sleeping Accommodation
- E-Books: Mental health at work series
- E-Books: Live Fire Training: Principles and Practice
- E-Books: Pre-Startup Safety Review Guide
- E-Books: Fire and Emergency Drill Manual and Building Inspection Guide
- E-Books: Health and Safety: Risk Management 5th edition
- E-Books: Fire Protection systems -Third edition 2021
- E-Books: Fire Safety Logbook templates
- E-Books: From Accidents to Zero
- E-Books: Electric Safety Practice and Standards
- Your steps to chemical safety
- E-Books: Ergonomics and Psychology Developments in Theory and Practice
- E-Books: HAZOPS Should BE fun-The Stream-Based HAZOP
- E-Books: Safety Health and Environmental Auditing
- E-Books: A Quick Guide to Health and Safety
- E-Books: Occupational Ergonomics A Practical Approach
- E-Books: Job Hazard Analysis A Guide for Voluntary Compliance and Beyond
- E-Books: Electrical Safety of Low Voltage Systems




