Introduction to Health and Safety in Construction has quickly established itself, in its first two years, as the standard text for students taking the NEBOSH National Certificate in Construction Safety and Health. It is also of great value to those working in the construction industry at all levels, particularly construction site managers and foremen. As it has become a significant work of reference for managers with health and safety responsibilities, it is a matter of prime importance that it should be kept up to date, as far as is possible, with new legislation and recent developments. There has been concern for some time at the poor record of health and safety in the construction industry and although performance has got better over recent years, there is still room for improvement. The legal health and safety requirements for all places of work are numerous and complex; it is the intention of the authors to offer an introduction to the subject for all those who have the maintenance of good health and safety standards as part of their employment duties or those who are considering the possibility of a career as a health and safety professional. Health and safety is well recognized as an important component of the activities of any organization, not only because of the importance of protecting people from harm but also because of the growth in the direct and indirect costs of accidents. These costs have increased more dramatically than the rate of retail price inflation by a considerable amount in the last few years as the number of civil claims and awards have risen each year.
It is very important that basic health and safety legal requirements are clearly understood by all organizations
whether public or private, large or small. A good health and safety performance is normally only achieved when health and safety is effectively managed so that significant risks are identified and reduced by adopting appropriate high quality control measures.
Introduction to Health and Safety in Construction is based on the QCA (Qualification and Curriculum Authority) accredited NEBOSH Certificate in Construction Safety and Health syllabus as revised in August 2003. It has been developed specifically for students who are studying for that NEBOSH National Certificate course. It was felt appropriate to produce a text book that mirrored the Construction Certificate syllabus in its revised unitized form and in a single volume to the required breadth and depth. The syllabus, which follows the general pattern for health and safety management set by the Health and Safety Executive in their guidance HSG 65, is risk and management based so it does not start from the assumption that health and safety is best managed by looking first at the causes of failures. Fortunately, failures such as accidents and ill health are relatively rare and random events in most workplaces. A full copy of the syllabus and guide can be obtained directly from NEBOSH.
This second edition has been produced in order to update the health and safety legislation, with particular regard to changes in legislation relating to fire – the Regulatory Reform Fire Safety Order 2005. This removes the requirement for fire certificates and revokes the Fire Precautions Act 1971 and the Fire Precautions (Workplace)
Requirements. This additional information enables the book to be useful to students undertaking the new NEBOSH Certificate in Fire Safety and Risk Management.
Other important changes in health and safety legislation, which are included in this edition, are the Work at Height Regulations, the Control of Vibration at Work Regulations 2005, the Control of Noise at Work Regulations 2005, the draft Control of Asbestos Regulations 2006, the Hazardous Waste (England and Wales) Regulations 2005 and the Introduction of Workplace Exposure Limits (WELs) in the 2005 amendments to the COSHH Regulations.
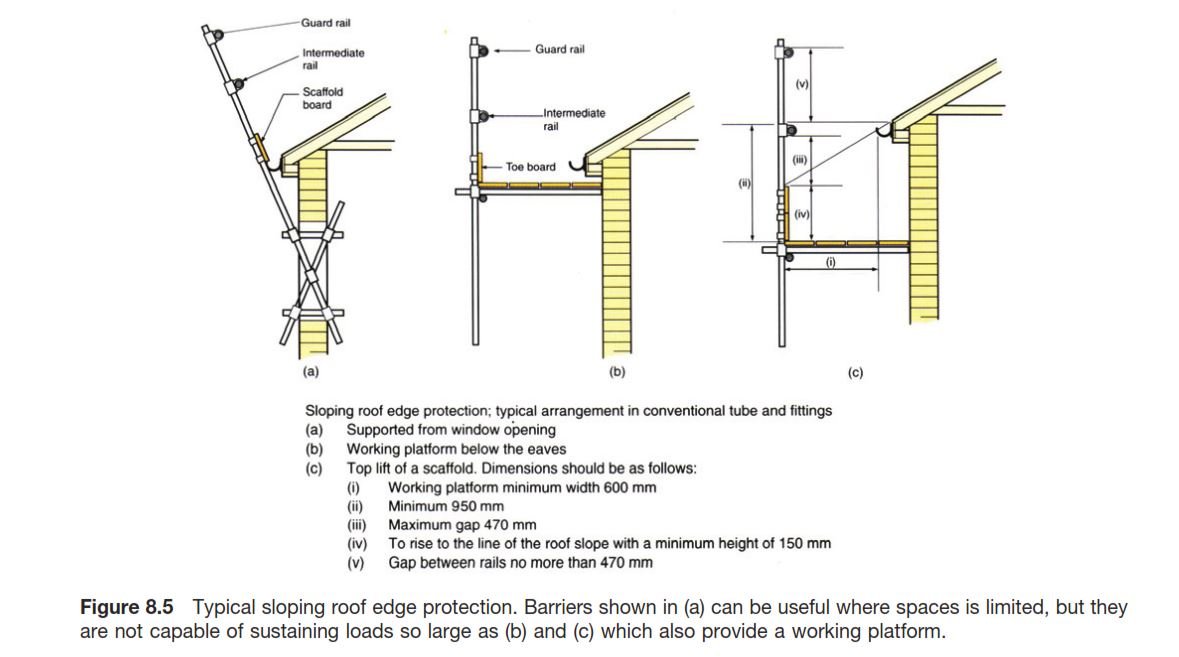
Table of Contents
PREFACE
xiii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
xv
ABOUT THE AUTHORS
xvi
LIST OF PRINCIPAL ABBREVIATIONS
xvii
ILLUSTRATIONS CREDITS
xix
1 HEALTH AND SAFETY FOUNDATIONS
1
1.1 Introduction
1
1.2 Some basic definitions
2
1.3 The legal framework for health and safety
3
1.4 The legal system in England and Wales
4
1.5 The legal system in Scotland
5
1.6 European Courts
5
1.7 Sources of law (England and Wales)
6
1.8 Common law torts and duties
7
1.9 Levels of statutory duty
7
1.10 The influence of the European Union (EU) on health and safety
8
1.11 The Health and Safety at Work Act 1974
10
1.12 The Management of Health and Safety at Work Regulations 1999
13
1.13 The main legal instruments relating to construction work
13
1.14 Role and function of external agencies
14
1.15 The scope and definition of construction
15
1.16 The health and safety problem in the construction industry
15
1.17 Moral, legal and financial arguments for health and safety management
16
1.18 The framework for health and safety management
19
1.19 Practice NEBOSH questions for Chapter 1
21
2 POLICY
23
2.1 Introduction
23
2.2 Legal requirements
23
2.3 Key elements of a health and safety policy
24
2.4 Review of health and safety policy
25
2.5 Practice NEBOSH questions for Chapter 2
27
Appendix 2.1 – Health and Safety Policy checklist
3 ORGANIZING FOR HEALTH AND SAFETY
31
3.1 Introduction
31
3.2 Control
32
3.3 Employers’ responsibilities
32
3.4 Employees’ responsibilities
32
3.5 Organizational health and safety responsibilities
33
3.6 Role and functions of health and safety and other advisers
34
3.7 Persons in control of premises
35
3.8 Self-employed
36
3.9 The supply chain
36
3.10 Contractors
38
3.11 Joint occupation of premises
44
3.12 Cooperation with the workforce
45
3.13 Practice NEBOSH questions for Chapter 3
46
Appendix 3.1 – Typical organizational responsibilities
47
Appendix 3.2 – Checklist for supply chain health and safety management
49
4 PROMOTING A POSITIVE HEALTH AND SAFETY CULTURE
51
4.1 Introduction
51
4.2 Definition of a health and safety culture
51
4.3 Safety culture and safety performance
52
4.4 Human factors and their influence on safety performance
53
4.5 Human errors and violations
57
4.6 The development of a positive health and safety culture
60
4.7 Effective communication
61
4.8 Health and safety training
62
4.9 Internal influences
64
4.10 External influences
65
4.11 Practice NEBOSH questions for Chapter 4
67
5 RISK ASSESSMENT
69
5.1 Introduction
69
5.2 Legal aspects of risk assessment
69
5.3 Forms of risk assessment
70
5.4 Some definitions
70
5.5 The objectives of risk assessment
72
5.6 Accident categories
72
5.7 Health risks
72
5.8 The management of risk assessment
72
5.9 The risk assessment process
73
5.10 Risk control measures
74
5.11 Hierarchy of risk control
75
5.12 Prioritization of risk control
75
5.13 Record of risk assessment findings
75
5.14 Monitoring and review
75
5.15 Special cases
76
5.16 Practice NEBOSH questions for Chapter 5
77
Appendix 5.1 – Hazard checklist
78
Appendix 5.2 – Example of a risk assessment record
79
6 PRINCIPLES OF CONTROL
81
6.1 Introduction
81
6.2 Principles of prevention
81
6.3 Hierarchy of risk control
82
6.4 Controlling health risks
85
6.5 Safe systems of work
87
6.6 Lone workers
90
6.7 Permits to work
90
6.8 Emergency procedures
94
6.9 First aid at work
95
6.10 Practice NEBOSH questions for Chapter 6
98
Appendix 6.1 – Fire notice
99
Appendix 6.2 – Job safety analysis form
100
Appendix 6.3 – Example of a safety method statement form
101
Appendix 6.4 – Essential elements of a permit-to-work form
102
7 GENERAL SITE ISSUES – HAZARDS AND CONTROL
103
7.1 Introduction
103
7.2 General hazards and controls
104
7.3 Initial site assessment
106
7.4 Site controls
107
7.5 Provision of welfare facilities
110
7.6 Practice NEBOSH questions for Chapter 7
111
Appendix 7.1 – A typical set of site rules
112
8 WORKING AT HEIGHT – HAZARDS AND CONTROL
115
8.1 Introduction
115
8.2 The Work at Height Regulations 2004 (WAHR)
115
8.3 Construction hazards and controls from working at height
117
8.4 Working above ground or where there is a risk of falling
121
8.5 Practice NEBOSH questions for Chapter 8
135
Appendix 8.1 – Inspection report form
137
Appendix 8.2 – Checklist of typical scaffolding faults
139
Appendix 8.3 – A checklist for a safety inspection of scaffold
139
Appendix 8.4 – Examples of safe systems of work used in roof work
140
9 EXCAVATION WORK AND CONFINED SPACES – HAZARDS
AND CONTROL
141
9.1 Introduction
141
9.2 Excavations – hazards and control
141
9.3 Confined spaces
150
9.4 Practice NEBOSH questions for Chapter 9
154
Appendix 9.1 – Inspection report for excavation
155
Appendix 9.2 – An example of safe digging practice
157
Appendix 9.3 – Typical excavation work risk assessment
158
Appendix 9.4 – Typical confined spaces risk assessment
159
10 DEMOLITION – HAZARDS AND CONTROL
161
10.1 Introduction
161
10.2 Principal hazards of demolition work
162
10.3 Pre-demolition investigation and survey
162
10.4 Demolition method statement
163
10.5 Management of the demolition and general controls
165
10.6 Specific issues
166
10.7 Practice NEBOSH questions for Chapter 10
168
Appendix 10.1 – Checklist for a safe system of work
169
11 MOVEMENT OF PEOPLE AND VEHICLES – HAZARDS
AND CONTROL
171
11.1 Introduction
171
11.2 Hazards to pedestrians
171
11.3 Control strategies for pedestrian hazards
173
11.4 Hazards to the general public and the associated controls in
construction activities, including street works
176
11.5 Hazards in vehicle operations
178
11.6 Control strategies for safe vehicle operations
179
11.7 The management of vehicle movements
180
11.8 Hazards and controls of vehicles on construction sites
181
11.9 Managing occupational road safety
182
11.10 Practice NEBOSH questions for Chapter 11
187
12 WORK EQUIPMENT HAZARDS AND CONTROL
189
12.1 Introduction
189
12.2 Suitability of work equipment and CE marking
189
12.3 Use and maintenance of equipment with specific risks
191
12.4 Information, instruction and training
191
12.5 Maintenance and inspection
192
12.6 Operation and working environment
193
12.7 Users’ and hirers’ responsibilities
194
12.8 Hand-held tools
195
12.9 Mechanical machinery hazards
197
12.10 Mobile work equipment
199
12.11 Non-mechanical machinery hazards
201
12.12 Examples of machinery hazards
201
12.13 Practical safeguards
203
12.14 Other safety devices
206
12.15 Application of safeguards to the range of machines
207
12.16 Guard construction
214
12.17 Practice NEBOSH questions for Chapter 12
214
13 MANUAL AND MECHANICAL HANDLING HAZARDS AND CONTROL
215
13.1 Introduction
215
13.2 Manual handling hazards and injuries
215
13.3 Manual handling risk assessments
217
13.4 Types of mechanical handling and lifting equipment
220
13.5 Requirements for the statutory examination of lifting equipment
229
13.6 Practice NEBOSH questions for Chapter 13
229
Appendix 13.1 – Manual handling of loads assessment checklist
231
Appendix 13.2 – A typical risk assessment for an excavator to be used for lifting
234
Appendix 13.3 – A typical risk assessment for the use of lifting equipment
235
14 ELECTRICAL HAZARDS AND CONTROL
237
14.1 Introduction
237
14.2 Principles of electricity and some definitions
237
14.3 Electrical hazards and injuries
239
14.4 General control measures for electrical hazards
244
14.5 The selection and suitability of equipment
245
14.6 Inspection and maintenance strategies
247
14.7 Portable electrical appliances testing
248
14.8 Protection against contact with live overhead power lines
251
14.9 Practice NEBOSH questions for Chapter 14
252
15 FIRE HAZARDS AND CONTROL
253
15.1 Introduction
253
15.2 The Regulatory Reform (Fire Safety) Order (RRFSO) – Requirements
254
15.3 Basic principles of fire
256
15.4 Methods of extinction
257
15.5 Classification of fire
258
15.6 Principles of heat transmission and fire spread
258
15.7 Common causes of fire and consequences
260
15.8 Fire risk assessment
261
15.9 Fire detection and warning
267
15.10 Means of escape in case of fire
268
15.11 Principles of fire protection in buildings
270
15.12 Provision of fire-fighting equipment
271
15.13 Maintenance and testing of fire-fighting equipment
272
15.14 Planning for an emergency and training staff
273
15.15 Fire procedures and people with a disability
273
15.16 Practice NEBOSH questions for Chapter 15
274
Appendix 15.1 – Fire risk assessment as recommended in Fire Safety Guides
275
Appendix 15.2 – Example form for recording significant findings as published in 2006
276
16 CHEMICAL AND BIOLOGICAL HEALTH HAZARDS AND CONTROL
277
16.1 Introduction
277
16.2 Forms of chemical agent
277
16.3 Forms of biological agent
278
16.4 Classification of hazardous substances and their associated health risks
278
16.5 Routes of entry to the human body
279
16.6 Health hazards of specific agents
283
16.7 Requirements of the COSHH Regulations
286
16.8 Details of a COSHH assessment
287
16.9 The control measures required under the COSHH Regulations
291
16.10 Health surveillance and personal hygiene
297
16.11 Maintenance and emergency controls
297
16.12 Control of asbestos
298
16.13 Environmental considerations
300
16.14 Practice NEBOSH questions for Chapter 16
302
17 PHYSICAL AND PSYCHOLOGICAL HEALTH HAZARDS AND CONTROL
305
17.1 Introduction
305
17.2 Task and workstation design
305
17.3 Work environment issues
313
17.4 Noise
314
17.5 Heat and radiation hazards
320
17.6 The causes and prevention of workplace stress
323
17.7 The causes and prevention of workplace violence
325
17.8 The effects of alcohol and drugs
328
17.9 Practice NEBOSH questions for Chapter 17
329
18 INCIDENT INVESTIGATION, RECORDING AND REPORTING
331
18.1 Introduction
331
18.2 Reasons for incident /accident investigation
332
18.3 Which incidents/accidents should be investigated?
333
18.4 Investigations and causes of incidents
334
18.5 Legal recording and reporting requirements
336
18.6 Typical examples of incidents within the construction industry
338
18.7 Internal systems for collecting and analysing incident data
338
18.8 Compensation and insurance issues
340
18.9 Practice NEBOSH questions for Chapter 18
340
Appendix 18.1 – Injury report form
342
Appendix 18.2 – Information for insurance/compensation claims
344
19 MONITORING REVIEW AND AUDIT
347
19.1 Introduction
347
19.2 The traditional approach to measuring health and safety performance
347
19.3 Why measure performance?
348
19.4 What to measure
349
19.5 Measuring failure – reactive monitoring
350
19.6 Proactive monitoring – how to measure performance
350
19.7 Who should monitor performance?
353
19.8 Frequency of monitoring and inspections
353
19.9 Report writing
353
19.10 Review and audit
355
19.11 Practice NEBOSH questions for Chapter 19
358
Appendix 19.1 – Workplace inspection exercises
359
Appendix 19.2 – Checklist of items to be covered in a
construction site inspection
360
20 SUMMARY OF THE MAIN LEGAL REQUIREMENTS
365
20.1 Introduction
365
20.2 The legal framework
365
20.3 List of Acts and Regulations summarized
366
20.4 Health and Safety at Work etc Act (HSW Act) 1974
368
20.5 Environmental Protection Act 1990
370
20.6 The New Roads and Street Works Act 1991
375
20.7 Control of Asbestos at Work Regulations 2002
378
20.8 Asbestos (Licensing) Regulations 1983 as amended in 1998
384
20.9 Draft Control of Asbestos Regulations 2006
386
20.10 Chemicals (Hazard Information and Packaging for Supply)
Regulations 2002
394
20.11 Confined Spaces Regulations 1997
397
20.12 Construction (Design and Management) (CDM) Regulations 1994 and
Amendment Regulations 2000
399
20.13 Draft Construction (Design and Management) Regulations 2006
404
20.14 Construction (Head Protection) Regulations 1989
411
20.15 Construction (Health, Safety and Welfare) (CHSW) Regulations 1996
411
20.16 Health and Safety (Consultation with Employees) Regulations 1996
415
20.17 Control of Substances Hazardous to Health Regulations (COSHH) 2002
and 2005 Amendment
416
20.18 Dangerous Substances and Explosive Atmospheres
Regulations (DSEAR) 2002
420
20.19 Health and Safety (Display Screen Equipment) Regulations 1992
423
20.20 Electricity at Work Regulations 1989
425
20.21 Employers’ Liability (Compulsory Insurance) Act 1969 and
Regulations 1998
427
20.22 Regulatory Reform (Fire Safety) Order 2005
429
20.23 Health and Safety (First Aid) Regulations 1981
437
20.24 Health and Safety (Information for Employees) Regulations 1989
438
20.25 Ionising Radiation Regulations 1999
438
20.26 Control of Lead at Work Regulations 2002
440
20.27 Lifting Operations and Lifting Equipment Regulations 1998
442
20.28 Management of Health and Safety at Work Regulations 1999
446
20.29 Manual Handling Operations Regulations (MHO) 1992
448
20.30 Control of Noise at Work Regulations 2005
451
20.31 Personal Protective Equipment at Work Regulations 1992
455
20.32 Provision and Use of Work Equipment Regulations 1998 (except part IV)
457
20.33 The Reporting of Injuries, Diseases and Dangerous Occurrences
Regulations 1995
462
20.34 Safety Representatives and Safety Committees Regulations 1977
464
20.35 Health and Safety (Safety Signs and Signals) Regulations 1996
465
20.36 Supply of Machinery (Safety) Regulations 1992
468
20.37 Control of Vibration at Work Regulations 2005
471
20.38 Workplace (Health, Safety and Welfare) Regulations 1992
473
20.39 Work at Height Regulations 2005
476
20.40 Other relevant regulations in brief
480
21 STUDY SKILLS
485
21.1 Introduction
485
21.2 Finding a place to study
485
21.3 Planning for study
485
21.4 Blocked thinking
486
21.5 Taking notes
486
21.6 Reading for study
486
21.7 Revision
486
21.8 Organizing information
487
21.9 How does memory work?
487
21.10 How to deal with exams
489
21.11 The examiners’ reports
490
21.12 Conclusion
491
21.13 References
491
INDEX
493




