Safety interview Questions and Answers Part 2
11 min readSafety is a key concern in every workplace. Lives and livelihoods are at stake, not to mention thousands (or even millions) of dollars stemming from potential lost productivity and lawsuits.With that in mind, it’s important to start the process of ensuring safety as early as possible. At the beginning in fact, in the recruitment process.Think of the candidate interviews you do before any hire. The interview is an important step in getting to know your future employees. You get a chance to learn about their background, their work histories, even their personalities. But there is one subject that is often skipped at the interview stage: that’s right, safety.Here are below Safety technical Questions and it’s answers Part II support all Safety people during the Interview step :
28. What is the use of a film badge?
Ans: This badge will be worn by personnel, exposed to radiation due to their nature of duty and this is processed to calculate the received radiation dose of a person during the period (normally 1 month) of exposure.
29. What is a decay chart?
Ans: It is the chart showing the change in radioactivity of a source, for a period, at regular interval of time.
30. Who is an authorized exposed person?
Ans: He is one who got formal training in the used of sealed source and x-ray equipment used in industrial radiography.
- What are the requirements of a man basket?
Ans: It should be designed and fabricated according to standards, have third party certificate, two guide ropes, damage free lifting gears, the load bearing capacity should be written on the man basket, shackles with cotter pin only to be used.
- How are slings inspected?
Ans: All slings must be inspected before every use and periodically it should be inspected thoroughly and should be rejected, if found wear of one third the original outside diameter of outside individual wires, severe corrosion, distortion (kinking, crushing, bird-caging), broken wires (a maximum of 10 randomly distributed broken wires in one rope lay or 5 broken wires in one strand in one rope lay), heat damage (loss of internal lubricant by over heat exposure), pulled eye splices (any evidence that eye splices have been slipped, sleeves damage) deformation of wires and strands or pushed out of their original position and the sling should be clean from dirt or rust. Before use of the slings has to be color coded as per the month color code.
33. What are the requirements for a crane lifting?
Ans: Crane positioned on firm and level ground with wood pads and steel plates. Outriggers are fully extended, tires are off ground, certified operator and rigger are available, safe load indicator is working, the check list is filled with competent person, crane has a valid inspection sticker, insurance and third party certificate, the loads weight is confirmed and it is within the safe working limit of the crane, safety devices are not bypassed, the swing arm radius is barricaded and unauthorized people are evacuated, the lifting tools are free from defects, pads are used to protect the slings from load and vice-versa, wind speed is less than 32 kmh, approved lifting plan is available for critical lifts, permit for the activity is obtained, crane operators and riggers vision is not obstructed, the load is well balanced, and tag lines are used to control the weight etc.
34. What is working radius?
Ans: It is the maximum distance where the crane boom has to reach for lifting or lowering the load.
35. What is SWL?
Ans: Safe Working Load is the maximum load that can be applied to the lifting tool, safely.
36. What is lifting plan?
Ans: It is the document prepared for planning a critical lift by calculating and considering all factors which is going to effect the lift and there by selecting the correct tools and cranes and ensure the safe lifting procedure to be followed for the particular lift, giving details such as the size and weight of the object to be lifted, which crane is used for lifting and what the safety factor is, where the crane is positioned, from where the load is lifted, where it is fitted, size and SWL of each lifting tool used. And load chart is attached with it.
37. What is a excavation?
Ans: A man made cut, cavity, trench or depression formed by earth removal.
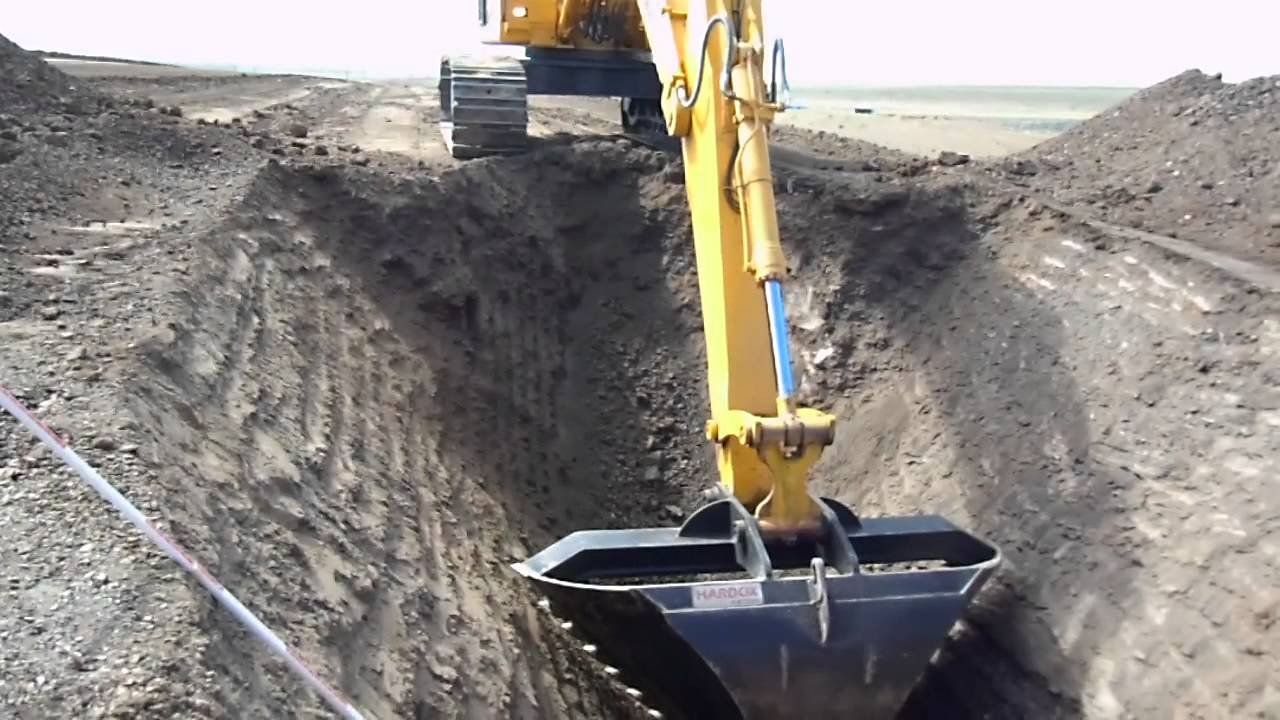

38. What is a trench?
Ans: A narrow excavation, where the depth is greater than the width.
39. What is shoring?
Ans: A structure that support the sides of an excavation and protect against cave-ins.

- What is the difference between a flash-back arrestor and a check valve?
Ans: A check valve allows flow in one direction only. This prevents oxygen reaching acetylene cylinder and acetylene reaching oxygen cylinder in the event of blockage in the torch or line or pressure variations.
But a flash back arrestor prevents reverse flow, stops the flow of flame from reaching the cylinder in the event of a flash back or the temperature exceeds a limit (220 deg F).
41. What are the classes of fire and what type of extinguishers are used for them?
Ans: Class A: Ordinary combustible materials
Ex: Paper, wood, cloth, plastic, rubber
Extinguisher- Water, DCP, Foam, CO2, Halon
Class B: Combustible liquids and gases
Ex: Gasoline, diesel, oil, grease, oil based paint, tar
Extinguisher- CO2, Foam, DCP
Class C: Energized electrical equipment
Extinguisher- DCP, FM-200, Halon, Carbon Dioxide
Class D: Combustible metals
Ex. Magnesium, Potassium, Zinc, Calcium, Sodium, Titanium
Extinguisher- Metal X-type, Combustible metal type.

- What are the responsibilities of a fire-watch?
Ans: Fire watch is a person designated to identify and eliminate fire hazards, alert and extinguish fire in case of any outbreak of fire and to protect the person and properties from a fire. He is the man to react first in case of fire by keeping a close watch on such hazardous areas. - What is color coding system?
Ans: This is the system followed to inspect and ensure the serviceability of tools, equipment’s periodically (normally it is monthly) like fire extinguishers, full body harness, lifting gears, electrical codes and cables, power tools, etc. These things are inspected by combatant person and are indicated by putting the color of particular month (this color is decided in advance and is being followed by all people at particular site). The items which are found defective or unserviceable will not be color coded and has to be removed from service. - Who can color code?
Ans: Competent Person.
- What is the maximum distance between two adjacent accesses in a long excavation?
Ans: A ladder must be present within 25ft., of employees working in excavation.
In open excavation – At every 30 meters on the perimeter, if less than 1.2 meters deep.
– At every 7.5 meters on the perimeter, if more than 1.2m deep. - What is an excavation considered as a confined space?
Ans: If depth is more than 1.2 meters. - Who can erect scaffolding?
Ans: Certified scaffolder. - Who can inspect the components used for erecting a scaffold?
Ans: A competent and certified scaffolding supervisor. - What is a tag system?
Ans: A tag is put on scaffolding, by a competent person, indicating the present condition whether it can be used and whether fall protection needed or not.
Red Tag: Do not use (Is being erected of dismantle)
Yellow Tag: Can be used with 100% fall protection (is incomplete or cannot be completed)
Green Tag: Safe to use (Scaffolding is complete) - Who can place a scaffold tag?
Ans: Competent person (Scaffolding Supervisor). - What are the details in a scaffolding tag?
Ans: Location, Maximum loading capacity (kN/m2 or psf); Date erected and date inspected with foreman’s name and signature. - In which conditions a scaffold cannot be erected?
Ans: Extreme weather (strong wind, rain, ice), ground not stable, safe clearance (minimum 10ft.) can’t be maintained with live wire, certified workers and supervisor are not available, permit not available. - What is the minimum overlapping of two adjacent planks in a scaffold platform?
Ans: Not less than 12 inches - What is a guard rail system?
Ans: A barrier consisting of top rails, midrails, toe boards and vertical uprights erected to prevent men and materials falling from an elevated work area.
- What is a toe board?
Ans: Barrier secured along the sides and ends of a platform to guard against falling of materials, tools, and other objects. - What is the minimum height of a toe-board?
Ans: 4 inches. - What is the height of top rail from platform?
Ans: 38 to 45 inches. - in what circumstances fall protection system to be used?
Ans: If a person could fall more than 1.8 meters then a fall protection system should be used.
E.g. any activity at an elevation more than 1.8 meters such an erection, dismantling or maintenance of scaffolding, pipes, equipment… - What is the minimum width required for a walk-way?
Ans. Minimum width of walk way is 18”.61. - What materials can be b placed on a scaffold platform?
Ans: All types of construction materials when is used for particular construction activity can be kept on scaffolding platform but before keeping the materials and tools required for the work on the platform, we must ensure load bearing capacity of that scaffolding platform. The platform shall not be over loaded and shall be fitted with falling object protection system like toe board, nets etc. - What are the minimum requirements for working on a scaffold?
Ans. Mobile scaffolding shall be plumb, level and square. It shall only be used and moved on a surface sufficiently firm and level to ensure stability. It shall be move only by manually pushing or pulling the base. No men equipment or materials shall be on the working platform or elsewhere on the scaffolding while it is in motion. Castor shall be locked at all times except during scaffold movement. The temporary foundation or track set on uneven ground for scaffold movement shall be level and properly secured. The height of the working platform shall not exceed 4 times of the minimum base dimension. If it exceed this limit outriggers must be installed. A complete guard rails system must be provided. The scaffolding shall be inspected and tagged before use by a competent person. - When should we inspect a scaffold?
Ans. A scaffold shall be inspected and tagged after completing erection. Also before each work period or where they are altered. Adjusted or subjected to rain or heavy winds.Thereafter the scaffold shall be examined at least once seven days. - With what color a ladder can be painted?
Ans. Aluminum ladders and wooden ladder shall notbe painted. - What is life line?
Ans. A life line is a component that consist of a flexible line that connects to an anchorage at one end to hang vertically or that connect to anchorages at both ends to stretch horizontally and which serves as method to connect other component of a personnel fall arrest system to the anchorage. - How can we calculate the safe anchorage of a life-line?
Ans. When life line is used they shall be fastened to fixed safe points of anchorage capable of supporting 2300 Kg. Shall be independent, and shall be protected from sharp edges and abrasion. Safe anchorage points may include structure members (minimum 4” structural member or 4” pipes) but do not include guard rails, vents, other small dia piping systems, electrical conduit, outrigger beams or counter weights. It shall be made from 10 mm dia. Width ropes. Horizontal life lines shall be installed at the highest feasible point, preferably above shoulder height. This life lines shall be maintained with unloaded sag at the centre no greater than 30 cm (12 inches) for e very 10 meters of life line length between attachment points
- What is Lock out/ Tag out system?
Ans. For servicing or maintenance of live equipment or pipe lines, where the unexpected energizing or release of energy could cause injury, lock and tag are placed on the isolating device to avoid uncontrolled operation and give details of the lock-out schedule.

- Expand the following:
•STARRT– Safety Task and Risk Reduction Talk
•COSHH– Control of substance hazardous to Health.
•OSHA– Occupational Safety and Health Administration.
•OSHAS– Occupational Health and Safety Assessment Series.
•ELCB – Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker.
•GFCI– Ground Fault circuit Interrupter.
•BS– British Standard \institute.
•SWL-Safe working Load.
•ANSI– American National standards Institute.
•LTI– Lost Time Incident.
•ASTM – American Society for Testing of Materials.
•JSA – Job Hazards Analysis.
•LEL – Lower Explosive Limit.
•UEL– Upper Explosive Limits.
•PEL– Permissible Explosive Limit.
•REL– Recommended Exposure Limit
•PSI– Pounds/Square Inch (1 bar= 14.7 psi)
•STEL– Short Term Exposure Limit.
•WBGT – Wet Bulb Globe Temperature
•APR – Air Purifying Respirator
•ASR – Air Supplying Respirator.
•SCBA– Self Contain Breathing Apparatus.
•RSO-Radiation Safety Officer
•NFPA– National Fire Protection association - What is the importance of a Tool box meeting?
Ans. The workers can be educated about safe rules and procedures, and their awareness can be improved on some special task its importance. - What is an Emergency Evacuation Plan?
Ans. It is the procedure to provide concise guide lines for evacuation in case of some emergency and to identify the emergencies in advance. This also helps us to plan and to define roles and responsibilities of all building custodian fire wardens and occupants. - What is a Hydro Test?
Ans. It is the test carried for leak test for pipes, equipment’s etc. by filling water in this equipment’s and pipes with some pressure and its joints and connection are checked for any leak or breakage. - What is a Hipot- Test?
Ans. It is the insulation leakage test done for high voltage electrical cables, with high voltage measure. - What are the safety requirements for doing a hot work?
Ans:
- a). Remove all combustible materials from the area(with 10 mm), possible.
b). Use fire blanket to protect immovable materials and also for welding slugs.
c). Cover the area with fire blanket for containment of park generated while doing hot work.
d). Provide proper fire extinguisher in sufficient numbers.
e). Appoint a fire watch with red jacket, If necessary.
f). Barricade the area and post proper signage.
g). Use of proper PPE and damage free tools and equipment.
h).Obtain a valid hot work permit.
i). Conduct gas test if presence of combustible gases expected prior to work.
- What is a risk assessment?
Ans. risk assessment is a method of estimating the rate of risk of an activity, by classifying actual and potential consequences and finding out mitigating actions to limit that risk. - In what situation Ear protection is needed?
Ans. In areas, where sound pollution is more than 85 dBA. - What is the emergency evacuation procedure to follow in the event of gas release?
Ans: don’t get panic on hearing alarm.
Switch off all the equipment and energized circuits.
Observe the direction of wind flow, proceed out in the cross wind direction to the plant boundary fence and then proceed up wind.
Obey further instructions from emergency response team.
Resume work after getting clearance only.
76. What is an “Assembly Muster Point”?
Ans: The area determined and marked for assembly of people working in case of any emergency.




