Industrial operations can produce a wide range of pollutants that can harm public health and the environment. Particulate matter, sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide, volatile organic compounds, and hazardous air pollutants are examples of pollutants. To solve these environmental concerns, enterprises can install pollution control systems that decrease or eliminate pollutant emissions into the air, water, and soil. However, deploying these technologies can be costly in terms of both capital investment and ongoing operation and maintenance expenditures. In this article, we’ll look at how industries may weigh the costs and advantages of deploying pollution control systems, as well as highlight some of the most widely utilized technologies in the workplace.
Also Read: E-Books:Introduction to Environmental Management

Costs and Benefits of Pollution Control Technologies
Implementing pollution control technologies in industrial settings can involve significant costs, both in terms of capital investment and ongoing operation and maintenance expenses. For example, installing a scrubber to reduce sulfur dioxide emissions from a power plant can cost millions of dollars. Similarly, implementing a hazardous waste management system can involve significant expenses for purchasing equipment, training personnel, and complying with regulatory requirements.
Despite these costs, there are several benefits to implementing pollution control technologies in industrial settings. These benefits include:
- Improved environmental performance: By reducing or eliminating the release of pollutants, pollution control technologies can help industries improve their environmental performance and reduce their impact on the environment.
- Enhanced public perception: Implementing pollution control technologies can also improve the public perception of the company. Companies that are seen as proactive in addressing environmental challenges are more likely to be viewed positively by stakeholders, including customers, investors, and regulators.
Also Read: Air Emissions Mangement Tips
- Potential cost savings: Pollution control technologies can also lead to potential cost savings. For example, implementing energy-efficient equipment can reduce energy consumption and lower operating costs. Similarly, implementing a hazardous waste management system can reduce the risk of costly fines and legal liabilities associated with improper disposal of hazardous waste.
Strategies for Balancing Costs and Benefits
Given the potential costs and benefits of implementing pollution control technologies, industries need to carefully balance these factors to ensure that they are making sound financial decisions while also protecting the environment and public health. Here are some strategies that industries can use to balance the costs and benefits of implementing pollution control technologies:
- Conduct a cost-benefit analysis: A cost-benefit analysis can help industries evaluate the potential costs and benefits of implementing pollution control technologies. This analysis should consider not only the direct costs of implementing the technology, but also potential savings from improved efficiency, reduced liability, and other indirect benefits.
- Seek external funding: Industries may be able to offset some of the costs of implementing pollution control technologies by seeking external funding. For example, many government agencies offer grants and loans to support environmental initiatives, and some utilities offer rebates or incentives for implementing energy-efficient equipment.
- Implement a phased approach: Implementing pollution control technologies can involve significant upfront costs. To minimize these costs, industries may consider implementing a phased approach that prioritizes the most critical areas for improvement first and gradually expands the scope of the program over time.
- Explore innovative financing options: Industries may also explore innovative financing options to help offset the costs of implementing pollution control technologies. For example, some companies may be able to finance equipment purchases through leasing or other financing arrangements, or partner with third-party providers who offer pollution control services on a performance-based contract.
Also Read: The Cost of Pollution: 1.7 Million Children Dead Each Year
Commonly Used Pollution Control Technologies
There is a wide range of pollution control technologies that industries can use to reduce their environmental impact. Here are some of the most commonly used technologies in industrial settings:
- Scrubbers: Scrubbers are devices that use a liquid to remove pollutants from industrial exhaust gases. The liquid absorbs the pollutants, which are then removed from the system. Scrubbers are commonly used to control emissions of sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and particulate matter (PM).
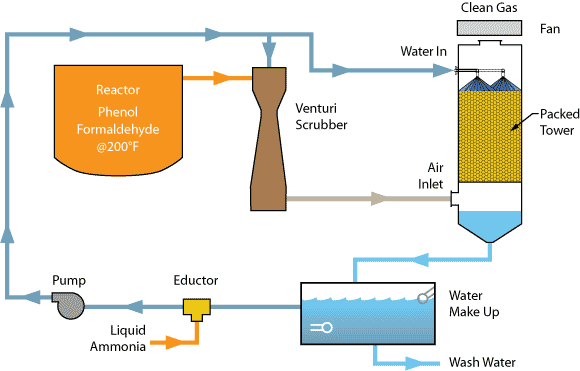
- Filters: Filters are used to remove particulate matter from industrial exhaust gases. They work by trapping the particles on a filter medium, which can be made of fabric, ceramic, or metal. Filters are commonly used to control emissions of PM, including dust, smoke, and ash.
- Catalytic converters: Catalytic converters are devices that use a catalyst to convert harmful pollutants into less harmful substances. They are commonly used to control emissions of NOx, carbon monoxide (CO), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
- Wet scrubbers: Wet scrubbers are similar to regular scrubbers, but they use water as the liquid medium. Wet scrubbers are commonly used to control emissions of acid gases, such as sulfur dioxide and hydrogen chloride.
- Thermal oxidizers: Thermal oxidizers are devices that use high temperatures to break down pollutants into less harmful substances. They are commonly used to control emissions of VOCs, which can be released during industrial processes such as painting and printing.
Also Reda: Sick building syndrome and Indoor Air Pollution
what Industrial Process
- Industrial processes involve the conversion of raw materials and other inputs into finished products through various physical, chemical, and biological processes. These processes can take place in a wide range of industries, including manufacturing, energy production, agriculture, and transportation.
- The specific processes used in industrial settings can vary depending on the industry and the product being produced. Some common industrial processes include:
- Chemical synthesis: Chemical synthesis involves combining different chemicals to create new substances. This process is commonly used in the production of pharmaceuticals, plastics, and other specialty chemicals.
- Mechanical processing: Mechanical processing involves using machinery to shape and form raw materials into finished products. This process is commonly used in manufacturing industries such as automotive and aerospace.
- Heat treatment: Heat treatment involves subjecting materials to high temperatures to alter their physical and chemical properties. This process is commonly used in the production of metals and alloys.
- Fermentation: Fermentation involves using microorganisms to convert organic materials into useful products such as food and beverages. This process is commonly used in the production of beer, wine, and cheese.
- Combustion: Combustion involves burning fuels to generate heat or electricity. This process is commonly used in energy production industries such as power plants and refineries.
- Extraction: Extraction involves removing valuable materials from raw materials using solvents or other chemical processes. This process is commonly used in the production of essential oils, fragrances, and flavors.
- Electrostatic precipitators: Electrostatic precipitators use an electric charge to remove particulate matter from industrial exhaust gases. The charged particles are attracted to oppositely charged plates, where they are removed from the system. Electrostatic precipitators are commonly used to control emissions of PM.
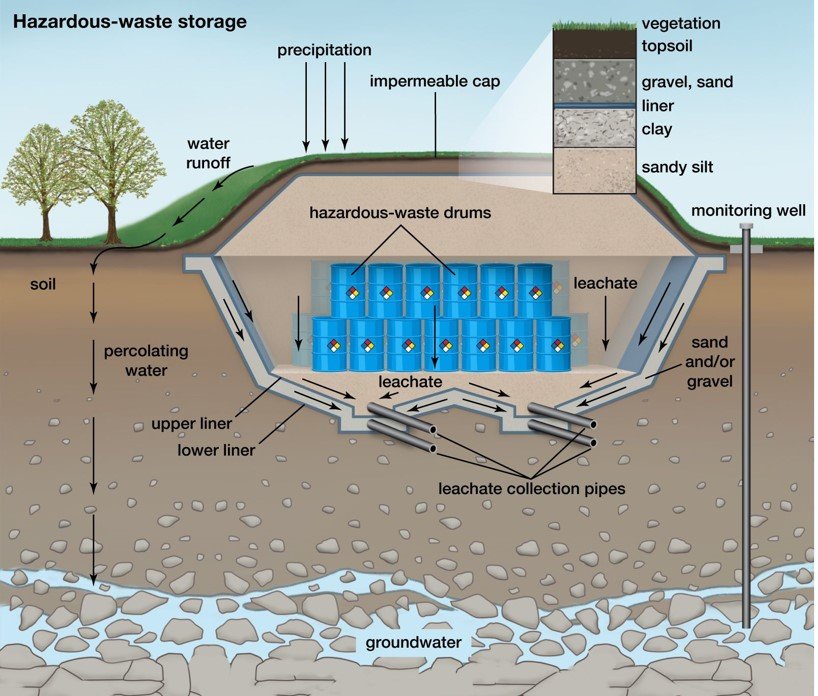
- Hazardous waste management systems: Hazardous waste management systems are designed to safely handle and dispose of hazardous waste generated by industrial processes. These systems can include storage facilities, treatment systems, and disposal methods that comply with regulatory requirements.

- Energy-efficient equipment: Energy-efficient equipment can help industries reduce their energy consumption and lower their operating costs. This can include equipment such as high-efficiency boilers, motors, and lighting systems.
- Sustainable production practices: Sustainable production practices, such as eco-design, life cycle assessment, and sustainable supply chain management, can help industries reduce their environmental impact and improve their overall sustainability.
Also Read: https://hsseworld.com/stormwater-pollution-prevention-plan/
Challenges and Opportunities
Implementing pollution control technologies in industrial settings can come with its own set of challenges and opportunities. Here are some of the key considerations to keep in mind:
- Cost: As we’ve discussed, implementing pollution control technologies can involve significant costs. This can be particularly challenging for small and medium-sized enterprises that may not have the financial resources to invest in these technologies.
- Regulatory compliance: Industries must comply with a wide range of environmental regulations, which can vary depending on the industry and the jurisdiction. Compliance can be complex and time-consuming, and failure to comply can result in costly fines and legal liabilities.
- Technological innovation: As environmental challenges continue to evolve, industries must continually innovate and develop new pollution control technologies to address these challenges. This can create opportunities for companies that are able to develop and commercialize new technologies.
- Public perception: Industries that are seen as proactive in addressing environmental challenges are more likely to be viewed positively by stakeholders, including customers, investors, and regulators. On the other hand, industries that are perceived as being indifferent to environmental concerns may face reputational risks and public backlash.
Also Read: EPA: Air Emissions of Toxic Chemicals from Industrial Facilities Down More Than Half Since 2005
Conclusion
Pollution control technologies play an important role in helping industries reduce their environmental impact. While implementing these technologies can involve significant costs, the benefits can be substantial, including improved environmental performance, enhanced public perception, and potential cost savings. To balance the costs and benefits of implementing pollution control technologies, industries can use strategies such as conducting a cost-benefit analysis, seeking external funding, implementing a phased approach, and exploring innovative financing options. By implementing these technologies and strategies, industries can help protect the environment and public health while also ensuring their long-term financial viability.
Also Read:
For more safety Resources Please Visit Safetybagresources