In any industrial or commercial setting, preparedness isn’t just a policy; it’s the bedrock of a safe environment. While we hope to never face a fire, having the right fire safety products in place is a non-negotiable part of responsible facility management. These tools are your first, and often most crucial, line of defense in protecting lives, assets, and business continuity.
However, the world of fire safety equipment is vast and varied. A fire extinguisher that’s perfect for an office is dangerously ineffective in a commercial kitchen. This is where a strategic approach to selecting your safety solutions becomes paramount. This guide is designed for engineers, facility managers, and decision-makers like you. We’ll break down the core categories of fire safety products, explore how to match them to specific environments, and discuss the critical importance of regular maintenance.

A collection of essential fire safety products ready for use.
The Core Categories of Firefighting Equipment
Not all fires are the same, which is why there isn’t a single, one-size-fits-all solution. Effective fire safety relies on a layered system of different products working together. Let’s break down the primary categories.
1. Fire Extinguishers: Your First Line of Defense
When a small fire starts, a portable extinguisher is often the first tool used to prevent it from escalating. However, using the wrong type can make the situation worse. Extinguishers are classified based on the type of fire they are designed to fight:
- Class A: For ordinary combustibles like wood, paper, and plastic.
- Class B: For flammable liquids such as gasoline, oil, and grease.
- Class C: For fires involving energized electrical equipment.
- Class D: For combustible metals, typically found in industrial settings.
- Class K: Specifically for fires in commercial kitchens involving cooking oils and fats.
Read:Fire Extinguisher Classification Meaning
Most commercial buildings use versatile ABC extinguishers, but specialized environments require specific solutions.
2. Fire Suppression Systems: Automated 24/7 Protection
For situations where a fire can start unnoticed or spread rapidly, automated fire suppression products are essential. Think of these as an automated firefighter on duty around the clock.
- Sprinkler Systems: The most common type, these systems automatically detect heat and release water to control or extinguish a fire.
- Clean Agent Systems: Used in areas where water would cause catastrophic damage, such as data centers or archives. These systems deploy a gas (like FM-200 or Novec 1230) that removes oxygen or heat to suppress the fire without leaving a residue. These are key pieces of industrial firefighting equipment.
3. Detection and Alarm Systems: The Power of Early Warning
You can’t fight a fire you don’t know about. Detection and alarm systems are the “eyes and ears” of your fire safety plan. These fire prevention products include:
- Smoke Detectors: The most common type, designed to sense smoke particles in the air.
- Heat Detectors: Used in dusty or steamy environments (like workshops or kitchens) where smoke detectors might trigger false alarms.
- Manual Pull Stations: Allow occupants to manually trigger the fire alarm system.
4. Evacuation and Personal Safety Equipment
When a fire is too large to fight, the priority shifts to safe evacuation. This category of fire and safety products is all about guiding people to safety.
- Emergency Lighting: Illuminates exit pathways during a power outage.
- Exit Signs: Clearly mark the routes to safety.
- Fire Blankets: A simple but effective tool for smothering small fires or wrapping around a person whose clothes have caught fire.
Read: Fire Emergency Evacuation Plan and the Fire Procedure
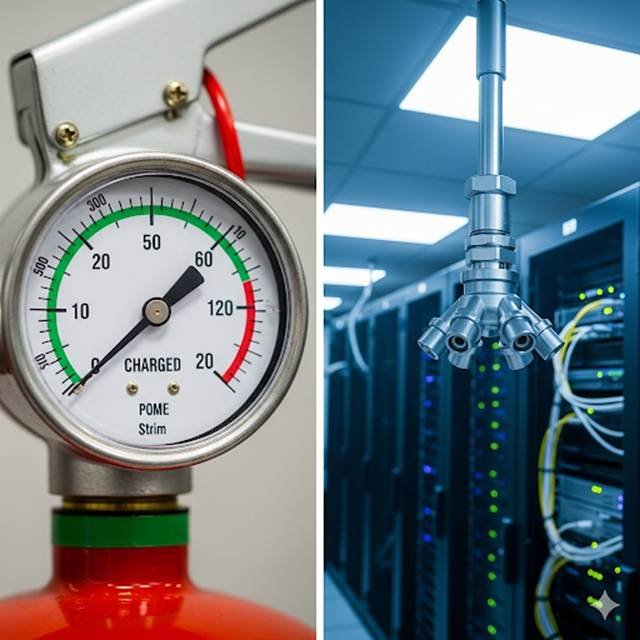

Comparing portable and automated fire safety equipment.
Choosing the Right Fire Safety Products for Your Environment
Understanding the categories is the first step. The next, more critical step is matching the right fire and safety equipment to your specific environment. Let’s look at a few common scenarios:
- For an office building: The primary risks are Class A (paper, furniture) and Class C (computers, wiring). A solid plan includes strategically placed ABC fire extinguishers, a network of smoke detectors, a sprinkler system, and clearly marked exit routes with emergency lighting.
- For a commercial kitchen: This is a high-risk zone for Class K fires. A standard ABC extinguisher won’t work effectively on a grease fire. The solution here is a combination of Class K extinguishers and an automated wet chemical suppression system installed in the ventilation hoods over the cooking appliances.
- For a manufacturing plant or warehouse: The needs here can be complex. You may have flammable liquids (Class B), energized equipment (Class C), and ordinary combustibles (Class A). This requires a zoned approach with different types of extinguishers, robust sprinkler systems designed for high-ceiling storage, and potentially specialized fire suppression products for high-hazard areas.
The Critical Role of Maintenance and Inspection
Purchasing high-quality fire safety products is only half the battle. A fire extinguisher with no pressure or a smoke detector with a dead battery is as good as having nothing at all. Regular inspection and maintenance are essential for two key reasons:
- Reliability: You need to be absolutely certain that your equipment will function perfectly in an emergency. Routine checks ensure that everything is in working order, from pressure gauges on extinguishers to the integrity of sprinkler pipes.
- Compliance: Regulatory bodies like the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) and the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) set strict standards for the inspection, testing, and maintenance of all fire protection equipment. Failing to comply can result in heavy fines and, more importantly, put your facility at risk.
Your maintenance schedule should include:
- Monthly visual inspections by in-house staff to check for obvious damage, blockages, or low-pressure gauges.
- Annual professional servicing by a certified technician who can perform detailed tests and maintenance.
- Keeping detailed logs of all inspections and service dates.
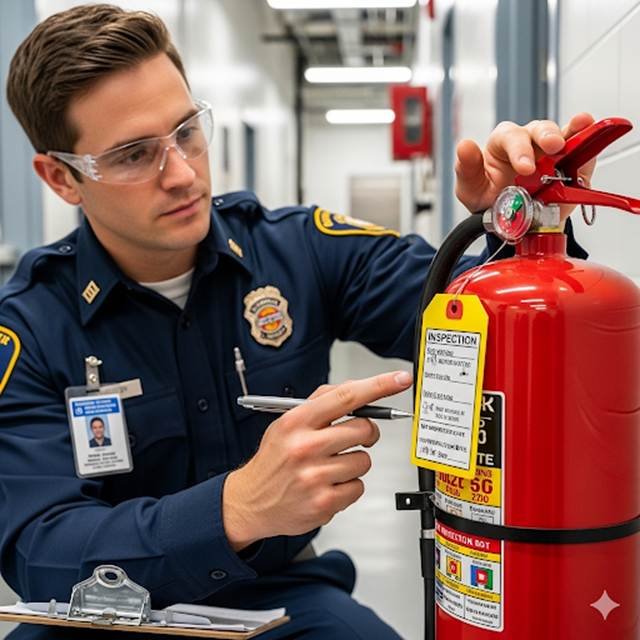

A professional conducting a fire extinguisher maintenance check.
Conclusion: Your Proactive Partner in Safety
Ultimately, a robust fire safety strategy is proactive, not reactive. It involves a thoughtful assessment of your unique risks and a commitment to investing in the right fire safety products to mitigate them. From the simple fire blanket to sophisticated industrial suppression systems, each piece of equipment plays a vital role in a comprehensive safety plan.
By understanding the core categories, matching the technology to the environment, and committing to a rigorous maintenance schedule, you transform your facility from a place that simply has fire safety supplies into a truly fire-safe environment.
Are you ready to enhance your facility’s safety and ensure you have the right solutions in place? Jia Yi Firefighting offers a complete range of certified fire protection equipment. Contact our experts today for a consultation and let us help you build a safer tomorrow.