Optimizing Diesel Refueling trucks Procedures for Construction
7 min readDiesel Refueling trucks play a critical role in construction sites, ensuring a steady supply of diesel fuel for equipment and vehicles. However, the refueling process itself poses various hazards that need to be carefully managed to maintain a safe working environment. Understanding these hazards and implementing proper safety measures is essential to protect personnel, prevent accidents, and minimize environmental risks. In this blog, we will explore essential safety practices to ensure diesel refueling truck safety at construction work sites.
Also Read: Photo of the day: Generator Safety

Common hazards associated with diesel refueling trucks and fueling process during construction projects
During diesel refueling activities in construction projects, several common hazards can be associated. These hazards include:
- Fire and Explosion: Diesel fuel is highly flammable, and any ignition source, such as sparks, flames, or electrical equipment, can lead to a fire or explosion. This risk is particularly high in the presence of fuel spills, inadequate grounding, or static electricity discharge.
- Fuel Spills: Spills can occur during the refueling process due to overfilling, improper handling of the fuel nozzle, or equipment/vehicle malfunction. Fuel spills pose slip and fall hazards, environmental contamination, and fire risks, and can contribute to air pollution.
- Inhalation and Skin Exposure: Diesel fuel vapors and fumes can be harmful when inhaled, leading to respiratory irritation, dizziness, or even long-term health effects. Skin contact with diesel fuel can cause irritation, dermatitis, or chemical burns.
- Environmental Hazards: Improper containment and management of fuel spills can result in environmental contamination, especially if the spills reach water bodies, soil, or vegetation. This can have severe ecological consequences.
- Electrical Hazards: Accidental contact between the fuel nozzle and electrical equipment, or failure to properly ground equipment during refueling, can result in electrical shocks or electrocution.
- Overpressurization and Bursting: In certain cases, overpressurization can occur in fuel tanks if the fuel is delivered too rapidly or if the tank venting system is not functioning properly. This can lead to tank bursting and fuel spraying, posing safety risks.
- Lack of Ventilation: Inadequate ventilation in the refueling area can result in the accumulation of fuel vapors, increasing the risk of fire or explosion.
- Slips, Trips, and Falls: Fuel spills on the ground or slippery surfaces can cause slips, trips, and falls, leading to injuries.
- Lack of Training and Awareness: Insufficient knowledge of proper refueling procedures, lack of awareness about potential hazards, and failure to follow safety protocols can increase the risk of accidents and injuries.
Also Read: Safety Flash: Reducing the risk of propane explosions in food trucks
Safe refueling Procedure
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
All personnel involved in the refueling process must wear the appropriate PPE, including but not limited to:
- Flame-resistant clothing
- Safety goggles or face shield
- Chemical-resistant gloves
- Safety footwear
Refueling Area Preparation:
- a. Designate a well-ventilated refueling area away from ignition sources, open flames, and electrical equipment.
- b. Ensure the refueling area is adequately marked with warning signs and barriers to prevent unauthorized access.
- c. Remove any potential sources of ignition, such as welding equipment or hot work, from the refueling area.
- d. Provide appropriate fire extinguishing equipment, such as fire extinguishers and fire blankets, nearby.
Diesel Storage Tank:
- a. Ensure the diesel storage tank is properly labeled and meets the standards set by OSHA.
- b. Regularly inspect the storage tank for leaks, damages, or signs of deterioration.
- c. Store the diesel fuel in a secure and well-ventilated area away from heat sources and direct sunlight.
- d. Follow proper procedures for filling and maintaining the storage tank, as per OSHA guidelines.
Refueling Process:
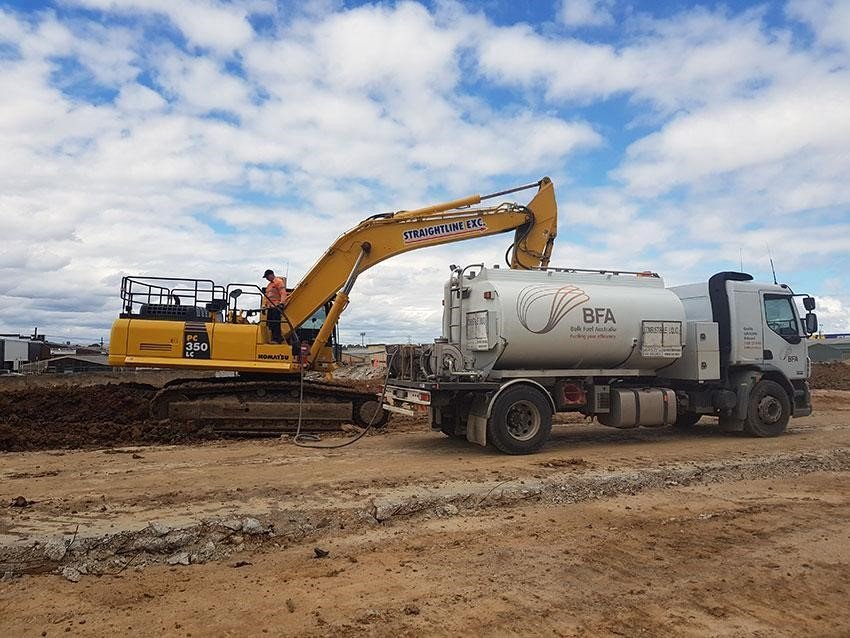

- a. Park the equipment or vehicle in the designated refueling area, ensuring it is turned off and the ignition is disabled.
- b. Ground the equipment or vehicle to prevent static electricity discharge.
- c. Use a dedicated and properly labeled diesel fuel nozzle for refueling.
- d. Insert the nozzle into the fuel tank and maintain contact throughout the refueling process to prevent spills and static buildup.
- e. Refuel the equipment or vehicle at a controlled and moderate pace to prevent overfilling and spills.
- f. Do not smoke or use open flames in the refueling area.
- g. Avoid using mobile devices or any other potential sources of ignition during the refueling process.
- h. After refueling, securely close the fuel tank cap or lid.
- i. Wipe off any spilled fuel and dispose of waste materials properly.
- j. Conduct a visual inspection for any leaks or spills before starting the equipment or vehicle.
Refueling Truck
Truck Conditions:
- Pre-Inspection:
a. Before commencing refueling activities, conduct a pre-inspection of the diesel refueling truck to ensure it is in proper working condition.
b. Check the truck’s fuel tank, hoses, nozzles, and valves for leaks, damages, or signs of wear and tear.
c. Verify that all safety equipment, such as fire extinguishers, spill kits, and grounding cables, are present and in good working condition.
d. Ensure that the truck’s emergency shut-off system is functioning correctly. - Vehicle Stability:
a. Ensure that the diesel refueling truck is parked on stable ground, with the parking brake engaged and wheels chocked to prevent accidental movement.
b. If the refueling truck is equipped with stabilizing outriggers, ensure they are properly deployed and secured. - Grounding:
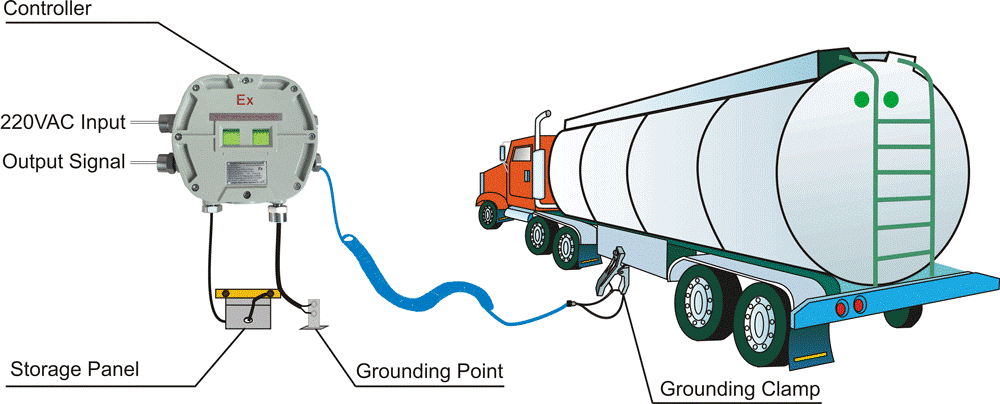
a. Properly ground the diesel refueling truck using grounding cables and clamps. Connect the clamp to a designated grounding point on the truck and attach the other end to a grounding rod or suitable grounding system.
b. Regularly inspect grounding cables for damages or signs of wear and tear.
Also Read: Powered Industrial Trucks
Personnel Competency:
- Training and Competency:
a. Ensure that personnel involved in diesel refueling activities during construction works have received appropriate training on fueling procedures, safety protocols, and emergency response.
b. Training should cover topics such as fire hazards, spill prevention and response, proper handling of fueling equipment, and personal protective equipment (PPE) usage.
c. Encourage personnel to attend refresher training sessions periodically to stay updated on best practices.
Emergency Procedures:
a. In the event of a fuel spill or leak, immediately notify the designated personnel and follow the established emergency response procedures.
b. If a fire occurs during refueling, activate the nearest fire alarm, evacuate the area, and use the available fire extinguishing equipment if it is safe to do so.
c. Provide first aid or medical assistance to any personnel injured during the refueling process, as required.
Emergency shut-off system for diesel refueling trucks
The emergency shut-off system for diesel refueling trucks is a critical safety feature that is designed to quickly and effectively stop the flow of fuel in case of an emergency or hazardous situation. This system is typically installed on the truck and is easily accessible to the operator or any personnel involved in the refueling process. Here are some key details about the emergency shut-off system:
- Purpose:
The primary purpose of the emergency shut-off system is to prevent fuel spills, mitigate fire risks, and protect personnel and the environment from potential hazards during refueling operations. It provides a rapid means of stopping the flow of fuel in case of an emergency, such as a fire, fuel leak, or other dangerous situations. - Location:
The emergency shut-off system is typically located near the refueling area on the diesel refueling truck. It is strategically positioned and easily identifiable, allowing operators or personnel to quickly access and activate the shut-off mechanism when needed. - Activation Mechanism:
The activation mechanism of the emergency shut-off system may vary depending on the specific design and model of the refueling truck. Common activation methods include manual switches, levers, or buttons that are easily accessible to the operator. Some systems may also include remote emergency shut-off options for additional safety measures. - Fuel Flow Interruption:
When the emergency shut-off system is activated, it immediately interrupts the flow of fuel from the tank to the dispensing nozzle. This rapid cessation of fuel flow helps prevent fuel spills or leaks, minimizing the risk of fire or environmental contamination. - Integration with Other Safety Systems:
In many cases, the emergency shut-off system is integrated with other safety systems on the diesel refueling truck. For example, it may be linked to the truck’s fire suppression system, allowing for automatic activation of fire suppression measures when the emergency shut-off is engaged. - Regular Testing and Maintenance:
To ensure the effectiveness of the emergency shut-off system, it is essential to conduct regular testing and maintenance. This includes routine inspections, verifying the proper functioning of the activation mechanism, and promptly addressing any issues or malfunctions that are identified. Regular testing and maintenance help ensure that the system is always ready to be activated when necessary.
Conclusion:
Diesel refueling trucks are vital for construction work sites, but safety should always be a top priority. By conducting regular inspections, establishing dedicated refueling areas, implementing proper grounding and bonding, providing comprehensive employee training, and enforcing the use of personal protective equipment, construction companies can ensure the safe operation of diesel refueling trucks. By prioritizing safety, we can minimize hazards, protect workers, and maintain a secure work environment in construction projects.
Read Also: Gasoline Safety Tips
For more safety Resources Please Visit Safetybagresources



