Q:How does dehydration impact workplace safety?
How Does Dehydration Occur?
Most commonly (but not exclusively), dehydration happens in hot working environments such as construction work during summer months or working inside a steel foundry.
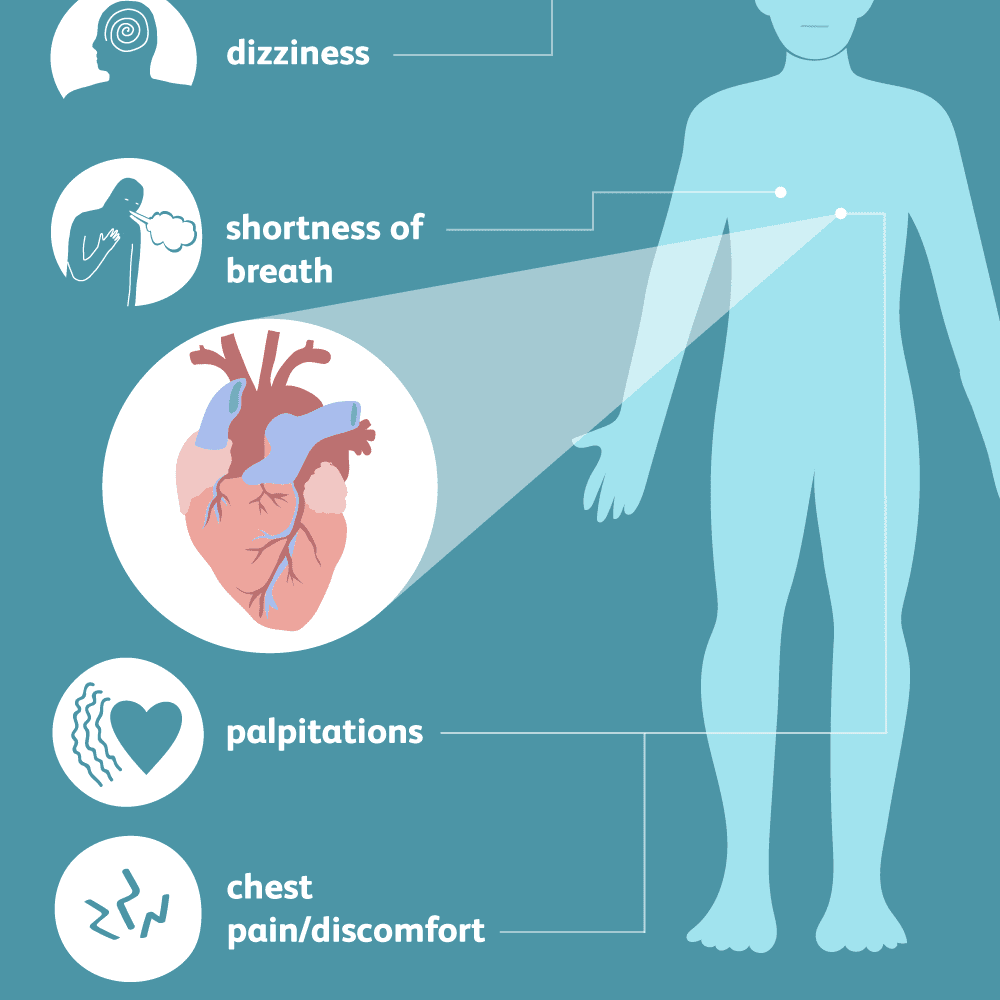
Dehydration can also occur when we’re doing intense physical activity where muscle contractions generate a substantial amount of body heat. In order to cool down and dissipate all the extra heat, the body perspires. The perspiration traps the heat and then allows it to escape through evaporation. When severely dehydrated due to lack of fluid, perspiration ceases and the body is left without its cooling mechanism. This can cause severe heat stress that, if not immediately addressed, could lead to headaches, lightheadedness, loss of consciousness, or other severe complications that could eventually be fatal.
What Happens When We’re Dehydrated?
Harm from dehydration is not limited to only these immediate physical effects.
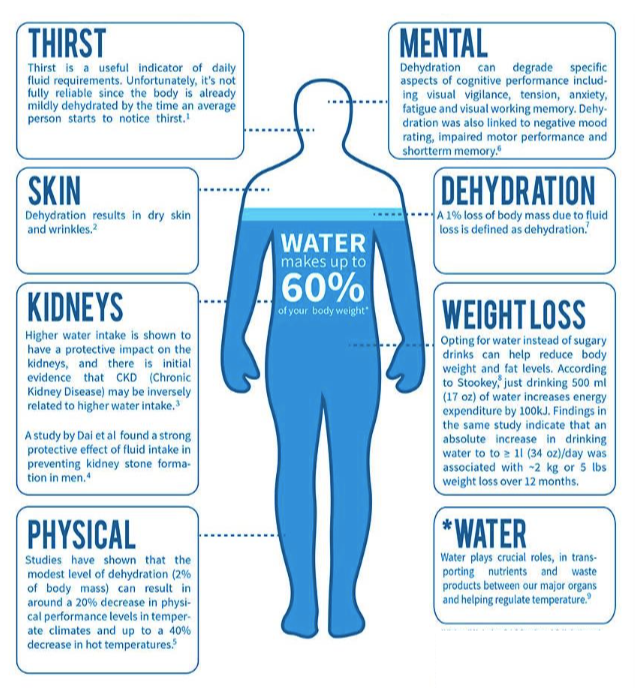
Research indicates that dehydration decreases brain tissue fluid, which in turn can result in changes in brain volume. This is probably why dehydration leads to lower mental performance. 1% dehydration (or a loss of 800 ml of fluid in a 80 kg individual) has been linked to a 12% decrease in employee productivity and a 3%-4% dehydration results in 25-50% decline in employee performance.
Dehydration slows your reaction time in the same way as impairment. A 3% dehydration has the same effect on a person’s reflexes as a 0.08 blood alcohol content, making errors in judgment and reaction time significantly more likely.
Dehydration and heat stress are two sides of the same coin. NASA determined that an employee that usually works at 80ºF (27ºC), if exposed to temperatures of 95ºF (35ºC), will make 12 times more errors compared to the work performance at the temperature they were accustomed to, and many of these errors translate to an increase in injury rate.
This begs the question of whether or not dehydrated employees should be trusted to operate heavy equipment and dangerous tools, direct traffic, or perform any high hazard activity. Not being able to properly assess the hazards in the workplace is a major source of accidents and injuries. As a result, dehydration is a special concern for health and safety practitioners.
Is Drinking Water Enough?
Knowing the severe mental and physiological effects of dehydration, we would expect most of us would do a good job staying hydrated throughout the day. While most of us might think that we do fairly well, the studies show that up to 80% of the adult U.S. population goes through at least part of their day (at least) mildly dehydrated – and consider that many of those people likely aren’t working at physical jobs in hot environments!
While water may be optimal for hydration in office workers, for those who are sweating at a high rate, research suggests that it isn’t enough. Sweat contains electrolytes, which need to be replaced for optimal hydration and performance. Severe climates and intense work conditions will put workers in greater danger of dehydration requiring more to be replaced than just water for complete hydration. If you working in these type conditions or if you fall into any of the following circumstances, you should consider a fluid with electrolytes to boost the minerals in your body